What is TPE? Can you think of a manufacturing material that is so flexible it stretches like rubber and molds like plastic? That’s TPE, or thermoplastic elastomer. It combines the properties of rubber with its softness and stretchability, and the properties of plastic with its recyclability and efficiency.
TPE’s functionality gave it a crucial role in the manufacturing industry. In this article, we will explore the properties, types, and applications of TPE to find out more about this material that helps shape the modern manufacturing world today.
What is a Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE)?
TPE is a material with a unique combination of the functionality and recyclability of plastics and the flexibility and stretchability of rubber. Its capability to bend like rubber but also be melted like plastic makes it so functional and cost-effective, and an ideal material for modern manufacturing industries today.
Thermoplastic Elastomer is made by blending hard thermoplastics and soft and rubbery elastomers. These materials are combined by melting. This creates a flexible, durable product that can be softened repeatedly by heating so it can bend and be used again for other processes.
Common Properties of Material TPE

Let’s talk about the common properties of TPE that are really useful.
Mechanical Properties
Hardness
A key property to consider when choosing a TPE is hardness, to gauge how firm or soft the material feels. TPE's hardness can be measured using a tool called a Shore durometer. It presses into the material to record the depth of indentation. This tool has different scales depending on the material’s softness and toughness. The Shore scale serves as an indication of how rigid or cushiony the TPE should be.
Tensile Properties
Given the flexible quality of TPEs, you still might want to know how much they stretch, and that’s when we start to talk about the tensile properties. They help us determine how a TPE reacts when it’s being stretched, pulled, and even strained.
Testing the tensile strength, samples are pulled until they snap. It is measured in megapascals (MPa). The higher the result, the tougher the TPE.
Compression Set
Another important factor to consider is the compression set. It’s a way to find out if the material will go back to its original form when the pressure is gone.
The compression set will tell you how much the material stays compressed after it gets released. The result is measured in percentage, and the lower the percentage, the better the material is.
This property should not be overlooked if the need is specifically for sealing applications where you need the material to keep a tight seal. TPEs with low compression sets are dependable because they can withstand pressure to keep their shape to serve their purpose.
Electrical Properties

Electrical Insulation
In simple terms, electrical insulation means that electricity will not pass through the material easily. In addition to being an important property, it also pertains to safety when using around electrical components.
Due to the good electrical insulating properties of many types of TPEs, they are often used to coat wires and cables, make connectors, and build housings.
Voltage Resistance
This electrical property makes it an important factor when we want to consider safety.
Having high voltage resistance means the material can block electricity even at high voltages without breaking down. That being said, the material reduces fire risk and electrical shock.
As a result of its good performance in this area, TPE has long been used as an electrical insulation material for wires, connectors, plugs, and other devices.
Thermal Properties

Temperature Resistance
TPE is a valuable material used in different settings and environments, so its heat resistance is a crucial factor to consider. The heat the material can withstand depends on exposure, the kind of stress, and even its shape.
For instance, in high-temperature settings like the engine compartment of a vehicle, the material must be strong enough to withstand elevated temperatures.
Shrinkage
Shrinkage happens when the material reduces its size or dimension during the process of cooling after being heated. During the transition from molten to solid state, polymers undergo thermal contraction as a natural reaction.
Shrinkage cannot be easily seen, but it’s still a factor to consider because it can still affect the final application. TPEs shrink based on composition; that’s why it is definitely important to ask your suppliers to know if the material will fit your needs.
Types of TPEs
TPE is not a universal material. It comes in a range of distinct types. Each type is engineered to bring distinct characteristics, tailored to your specific needs.
Understanding the types of TPE will help you choose the right fit for a specific application.
Styrenic Block Copolymers (SBC/TPE-S/TPS)

The most common type is TPE-S. It provides outstanding elasticity and simple, uncomplicated processing. It is widely used for seals, shoe soles, and packaging.
Thermoplastic Polyolefin Elastomers (TPO/TPE-O)
Popular for its chemical resistance properties, this type is strong but light. It is commonly used in auto parts like bumpers and interior trims.
Thermoplastic Vulcanizates (TPE-V/TPV/EA)
This type has the combined rubber elasticity with thermoplastic moldability. TPVs are durable and high-heat resistant, which makes them suitable for engine compartment parts and seals.
Thermoplastic Polyurethanes (TPU/TPE-U)
TPU has the durability to withstand damage due to friction and pressure. It is often used in medical devices, industrial belts, and even phone cases.
Thermoplastic Copolyester (COPE/TEEE/TPE-E)

TPC’s strength is its heat resistance and flexibility under pressure. This type is used in automotive tubing, electrical insulation, and power tools.
Thermoplastic Polyamides (PEBA/COPA/TPE-A/TPA)
This chemical and oil-resistant type of TPE is highly suitable for high-pressure environments like fuel lines, high-performance cables, and industrial applications.
Property Comparison of Different TPE Types
| Property | SBC | TPO | TPV | TPU | COPE | PEBA |
| Hardness | Soft to Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium to Hard | Medium to Hard | Medium |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate | Moderate | Good | High | High | High |
| Compression Set | Fair | Good | Very Good | Good | Good | Excellent |
| Electrical Insulation | Very Good | Good | Good | Moderate | Moderate | Good |
| Voltage Resistance | Good | Good | Good | Fair | Fair | Good |
| Temperature Resistance | Moderate (up to 90°C) | Moderate (up to 100°C) | Good (up to 150°C) | Good (up to 120°C) | Excellent (up to 180°C) | Excellent (up to 180°C) |
| Shrinkage | Low | Medium | Low | Low | Low | Very Low |
How are TPEs Processed?
Below are the usual ways you can choose to manufacture parts when the material you want to use is TPE.
Injection Molding
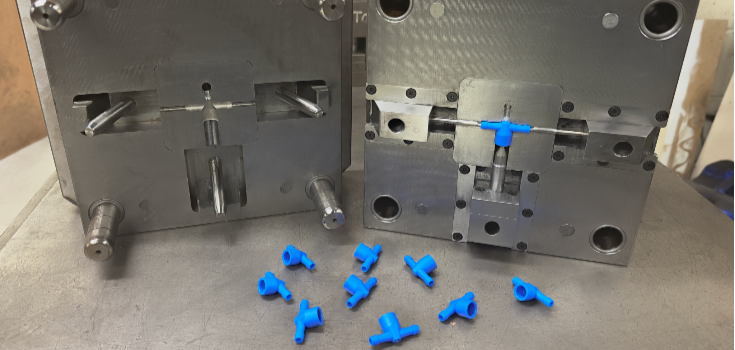
Injection molding is the most common method of processing TPEs. Pellets are typically heated and melted in barrels and transferred to molds to solidify. This type of process is preferred to mass-produce uniform shapes and sizes.
Extrusion
The same as the other process, the pellets are also melted in a heated barrel, but instead of being injected into a mold, they are pushed through a die, ideally to create tubes and sheets.
Extrusion Blow Molding
Extrusion blow molding is the process of shaping melted TPE into a hollow tube called a parison that is clamped into a mold and inflated with air until the desired shape is achieved. When the part has cooled and solidified, it is ejected from the mold.
3D Printing

3D printing method uses TPE filaments, and they are melted and extruded through a nozzle to build an object layer by layer. This is ideal for creating custom shapes and designs.
Advantages of TPE
These are the reasons why you can choose TPE as the material for your project:
Flexibility and Consistency
The ability to stretch and bend is what sets TPE apart from other materials, offering the flexibility of rubber and the durability of plastic. This advantage makes TPE an ideal choice for manufacturing industries that demand mass production and uniformity.
Chemical Performance
Most TPEs are resistant to oils and solvents, which allows them to maintain their form even in tough environments.
Versatility
TPE can be soft or firm depending on the manufacturing needs. Their versatility makes them the right choice for custom products to meet different needs.
Ability of Matching Color
Vibrant colors can be added to TPE to meet certain requirements or design ideas without the need to coat, which will cost extra.
Eco-friendly Property

The recyclability of TPEs makes it an eco-friendly choice because it reduces waste, as TPEs can be reprocessed and reshaped multiple times.
Cost Efficiency
The recyclability and flexibility reduce waste and costs to manufacturers, making TPE the perfect choice if they want to save on the costs of materials.
Disadvantages of TPE
You might also want to know the cons of using TPE, such as the following:
Lower Chemical Resistance
Some TPEs don’t react well to certain chemicals. It may cause them to wear out or break down easily in certain conditions. That means some TPEs may not be suitable for use when there will be contact with harsh industrial chemicals, automotive fluids, and cleaning agents.
Lower Heat Resistance
TPEs have a downside in terms of their ability to melt when exposed to heat. It means they have a lower ability to withstand high temperatures. This makes them prone to deformation and weakens the strength of a material. If used for automotive and industrial purposes, materials are usually exposed to high temperatures, and TPE might lose its functions or may even cause safety issues.
Creep
TPEs stretch and get deformed when exposed to stress and force, such as pulling or stretching, and that makes them unsuitable for parts that require them to be firm and steady
Cost

Compared to common plastics, the cost of TPEs is higher because of their complex production. And because of the costs, this may significantly impact the budget of manufacturing industries with massive production demands.
Adhesion Limitations
When used in manufacturing products, TPEs typically need to blend in with other materials. Other TPE types have adhesion as a disadvantage. And since they don’t blend well with other materials, they may not be suitable for products that demand durability and safety.
Moisture Sensitivity
For some TPEs, when not dried properly, the parts may bubble and be weak in form. Since they absorb moisture in the air, this is something to consider with careful handling and molding to get the desired results.
Is TPE safe?

TPEs can generally be referred to as safe, especially when they are medical or food grade, free of harmful additives, and used as intended.
Though TPE is considered safe, there are still considerations. Some can easily come in contact with harmful bacteria, and some types that easily wear may release or scrape harmful chemicals.
It is always good to consider factors like medical and food-grade labels, FDA approval, BPA-free labels, and reputable brands.
What is TPE Used for?
TPEs are quietly useful; you won’t even notice them in the items we’re using in our everyday lives. Their flexibility and purpose make them helpful in various industries.
Automotive
Heat-resistant TPEs are ideally used in engine compartments as sealants, gaskets, and bumpers.
Footwear & Consumer Products
From our comfy and bouncy shoe soles to the soft grip on tool handles, toothbrushes, and packaging, TPE made it possible. You’ll be surprised that it can also be found in household items. Even in diapers and toys.
Medical & Food
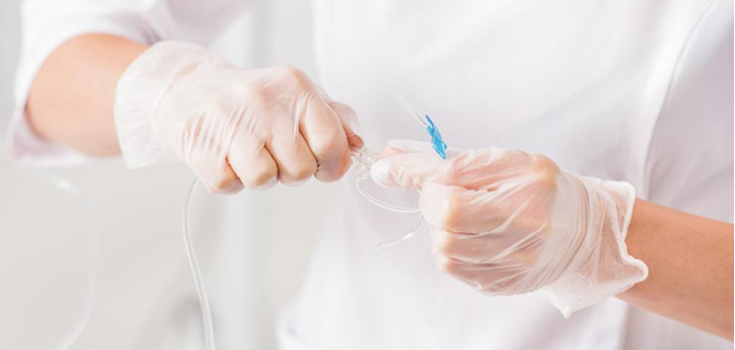
The medical-grade TPEs are used in items used in hospitals, like tubings, catheters, syringes, and medical films. While in the food industry, it can be found in food packaging and cooking tools.
Electronics & Industrial Use
TPEs are also useful in tech and industrial settings, providing cable coatings, electronic housings, and device cases.
Conclusion
True to its promise of versatility and strength, thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) truly helped industries come up with better manufacturing alternatives. From automotive and electronics to medical devices and consumer goods, various industries rely on TPE’s efficiency, convenience, and safety. The innovative approach to making it eco-friendly and sustainable made it an even better alternative.
If you are in need of high-quality TPE machined parts to fit your project needs, contact us today at DEK to explore how our product expertise can help you bring out the best in your projects.
FAQs
Are TPEs waterproof?
Yes, TPEs are waterproof and moisture resistant, making them more suitable for outdoor applications.
Can you color TPEs?
Yes, pigments can be added to the product to produce vibrant colors that will meet certain requirements.
What are medical grade TPEs?
Medical-grade TPEs had to go through strict safety standards to be used in medical supplies and devices.
When should I consider using TPEs?
Choose TPE when you are in need of a flexible and durable material that can be customized in color, shape, and firmness to meet your manufacturing needs.
