Computer-Aided Design has become one of the most necessary terms in modern engineering, architecture, and design. It allows experts to imagine, modify, and optimize their projects virtually before production starts.
By using CAD, industries save time, decrease errors, and improve product quality. CAD software has turned into a global standard throughout several fields, extending from engineering and construction to fashion and education.
What is Computer-Aided Design (CAD)?
Computer-Aided Design, also known as CAD, is the use of computer systems to help in the creation, adjustment, inspection, or optimization of a design. Instead of drawing manually on paper, CAD gives a digital environment where ideas can be created with precision. It improves exactness and enables professionals to create detailed models, technical drawings, and blueprints.
How Does Computer-Aided Design Work?

CAD works by a combination of hardware and software tools to create digital models of objects or structures. The user inputs design criteria into the software, which then creates a structural model.
CAD programs use mathematical algorithms and path-based graphics to simulate dimensions, materials, and margins. These models can be rotated, evaluated, and improved before they move to the manufacturing or construction phase.
Different Types of Computer-Aided Design
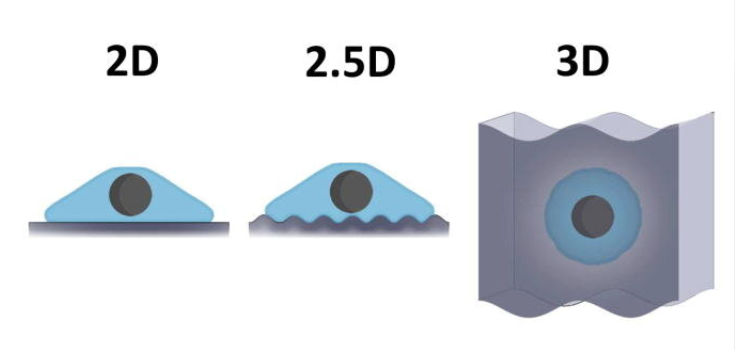
2D CAD
2D CAD was the initial model of CAD systems, launched in the 1970s by industries such as aerospace. At that time, companies needed a way to streamline recurring drafting tasks. 2D CAD gives a digital substitute for hand-operated drawing boards.
This system uses fundamental geometric shapes. For example, lines, arcs, circles, rectangles, and polygons can be used to create flat drawings. Engineers and architects depend on 2D CAD to produce arrangements, diagrams, section views, and vertical drawings. Annotation tools allow users to add dimensions, text, tables, and symbols for clarity.
Modern 2D CAD systems also have collections of standard components, smooth curves, curve segments, polylines, shading schemes, and automatic bill of materials generation. Popular examples include AutoCAD, CATIA, KeyCreator, and MEDUSA4.
Applications of 2D CAD:
- Building-related floor plans.
- Electrical system layouts.
- Mechanical part drawings.
- Civil engineering site layouts.
2.5D CAD
2.5D CAD is a combined system that resides between 2D and 3D. It represents objects with depth but not completely three-dimensional volume. This type of CAD is particularly significant in fabricating, PCB design, and manufacturing, where multi-level geometry or volume is required.
Common uses include:
- CNC machining routes
- Sheet metal cutting designs
- PCB board layouts
- Operational path generation
3D CAD
3D CAD is one of the most commonly accepted systems today. It allows creators to create accurate 3D models with depth, height, and width, empowering representation from every angle. Beyond geometry, 3D CAD software accommodates material modeling, load testing, and movement analysis.
Applications of 3D CAD:
- Car-making and aerospace product design.
- Consumer electronics.
- 3D printing designs.
- Construction design.
Software such as SolidWorks, CATIA, Siemens NX, and Autodesk Inventor lead this space.
Freeform CAD
Freeform CAD is needed when a standard structure cannot explain shapes. This is especially useful in industries that require organic forms. Alternatively to depending only on lines and curves, freeform CAD uses surface shaping and carving techniques.
Applications of Freeform CAD:
- Jewelry design.
- Fashion design.
- Industrial design.
- Character designing in games and animation
Examples: Rhinoceros 3D, Blender, Alias.
CAD File Formats
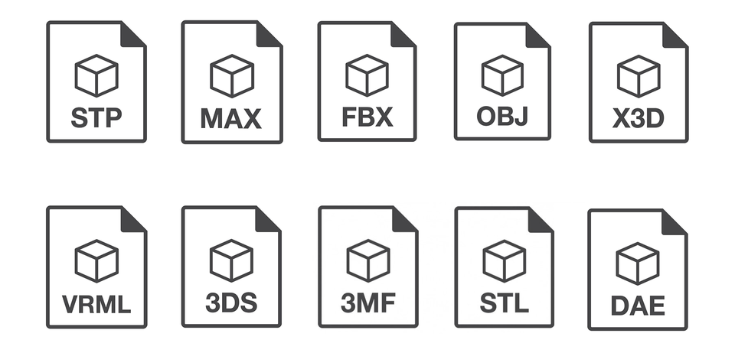
Neutral File Formats
Neutral formats are created to be shared across different CAD platforms without losing important data. These are widely used in cooperation between different organizations.
Native File Formats
Native formats are restricted to the software utilized to create them. Examples include DWG, SLDPRT, and RVT. While they maintain advanced features, they can generate consistency issues outside their native software.
Most Popular CAD Software and Tools

AutoCAD
AutoCAD is one of the popular CAD tools. It is commonly used in engineering, designing, and planning for both 2D and 3D modeling.
SolidWorks
SolidWorks is a variable-controlled 3D CAD software applied in machine-based design and product development. It provides modeling tools to test plans virtually.
CATIA
Dassault Systèmes created CATIA and is widely used in the aerospace and automotive industries. It enables complex designing systems and extensive designs.
Revit
Revit, developed by Autodesk, is a Building Information Modeling software used primarily by designers and construction experts for designing buildings and frameworks.
SketchUp
SketchUp is well-known for its ease of use in 3D modeling. It is broadly used in architecture, interior styling, and creative visualization projects.
Altium
Altium is a CAD software expert for printed circuit board design. It allows experts to create circuit diagrams and PCB designs.
FreeCAD
FreeCAD is an open-source CAD tool, compatible for mechanical engineering, product design, and structural modeling. It is adjustable and free for users who choose adjustable software.
What is Computer-Aided Design Used For?
Engineering Projects
CAD is widely utilized in engineering to create realistic mechanical parts, explore stress points, and simulate product performance before manufacturing.
Architecture and Interior Design
Architects use CAD to design blueprints, create floor plans, and imagine interior layouts. CAD ensures accuracy in building projects.
Manufacturing and Product Design
CAD helps in building models and designing new consumer products. Experts depend on CAD to make detailed models that lead to CNC machining.
CNC Machining
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines directly use CAD models to carve, cut materials with high accuracy.
Education and Training
CAD is taught in universities and technical institutes to train future experts, architects, and designers.
Automotive Industry
Car makers rely on CAD for vehicle design, air resistance testing, and safety models. It performs a significant role in the idea of cars and mass production.
Fashion Industry
The fashion industry uses CAD to design garments, textiles, and accessories. It authorizes designers to experiment with colors, patterns, and styles digitally.
Benefits of CAD

- Increased reliability in designs evaluated using hand-operated drafting
- Time productivity with sustainable templates and libraries
- Easy coordination via digital files
- The capability to simulate performance before manufacturing.
- Decreased material loss and production costs
- Help in creativity by allowing complicated shapes and ideas
Who uses CAD?
CAD is utilized by engineers, architects, drafters, interior designers, manufacturers, automotive designers, and jewelry makers. Approximately every advanced design industry integrates CAD in some way.
CAD Certificates
Popular certificates include Autodesk Certified Professional, SolidWorks Certification, and CATIA Certification. They show professional skills and increase professional opportunities.
Differences Between CAD and CAM
| Feature | CAD (Computer-Aided Design) | CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) |
| Purpose | Highlights on design and planning. | Focuses on constructing operations. |
| Output | 2D drawings, 3D models. | Machine toolpaths, CNC instructions |
| Users | Engineers, architects, designers | Operators, manufacturers |
| Core Function | Visualization, analysis, optimization | Material cutting, drilling, and machining |
| Software Examples | AutoCAD, SolidWorks, CATIA | Mastercam, Fusion 360, Edgecam |
CAD and CAM frequently work cooperatively in a single workflow. CAD controls the design, and CAM translates it into commands for manufacturing machines.
Conclusion
Computer-Aided Design has become an important part of advanced industries. It streamlines the design process, improves creativity, and ensures reliability throughout several applications.
If you are looking for expert support in CAD-related projects, DEK provides professional solutions customized to your needs. Contact us today and unlock the full possibility of CAD in your business.
FAQs
Are There Any Disadvantages of Using CAD?
Yes, disadvantages are high software costs, steep learning curves, and reliance on powerful hardware. However, the benefits often overtake these challenges.
What are the Skills Required for CAD?
Skills include technical drawing, structural comprehension, computer skills, attention to detail, and awareness of field-oriented CAD software.
Is CAD Hard to Learn?
CAD can be challenging at the initial stage, but with practice and proper training, it becomes controllable. Many software programs also offer tutorials, guides, and online learning materials.
