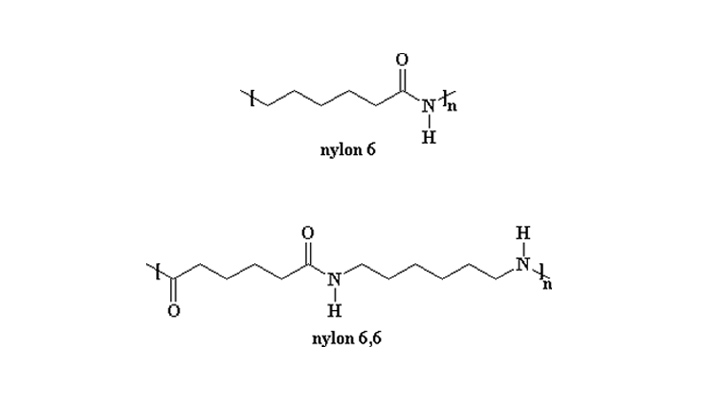
Nylon, also known as polyamide or PA, is a commonly used plastic processing material and the first synthetic fiber to appear in the world, composed of polyamide resins. It has excellent characteristics such as good wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc., and its value can be increased through modification, so it is widely used in daily life.
Therefore, this article will introduce you to different types of nylon, their specific properties, and applications, so that you can have a clearer understanding of the type of nylon you need!
Classification of Nyon by Source
Nylon can be classified into natural nylon and synthetic nylon according to its source.
Natural Nylon: Made directly from natural fiber materials extracted from animal and plant sources, such as cotton, wool, etc., processed into materials.
Synthetic Nylon: Made by synthesizing chemical raw materials extracted from petroleum and other chemical fuels.
Classification of Nylon by Polymer Structure
Nylon can be classified into saturated nylon and unsaturated nylon according to the polymer structure.
Saturated Nylon: All carbon-carbon bonds on the main chain of the molecule are single bonds, without double bond structures, which have higher strength and wear resistance but are relatively brittle.
Unsaturated Nylon: The main chain of the molecule contains double bond structures, usually with better flexibility and elasticity.
Classification of Nylon with Properties and Applications
Nylon can be classified into many different types according to its usage and properties. The following mainly introduces the properties and applications of 6 common nylon types.
Nylon 6(PA6)
Properties:
- Nylon is tough, with high tensile strength, elasticity and luster. The appearance of synthetic fibers is generally white.
- The toughness coefficient of nylon is 6.2–8.5 gf/D, with a density of approximately 1.13 g/cm³.
- It has a low friction coefficient and strong abrasion resistance. It also exhibits good chemical resistance, resisting certain chemicals, oils, and solvents.
- The melting point is approximately between 220-230°C, with a relatively high melting point and good heat resistance, maintaining structural stability in high-temperature environments.
- The typical water absorption rate is between 1% and 9%, indicating good water absorption properties, which may to some extent affect dimensional stability and mechanical properties.
Applications:
Automotive: Due to its excellent high strength, chemical resistance, and heat resistance, nylon is widely used in the production of automotive components, gears, and bearings.
Textile Industry: Due to its excellent tensile strength, lightweight, ease of dyeing, moldability, good elasticity, and strong abrasion resistance, Nylon 6 is commonly used in the production of fiber products such as clothing, fabrics, carpets, etc.
Industry: Due to its good toughness, nylon is often used to produce vacuum bag films for molding and packaging materials.
Electrical Industry: Due to its good insulation properties, nylon is commonly used in the production of electrical equipment parts such as plugs and sockets.
Nylon 66(PA66)
Properties:
- The hardness ranges between 70-85, making it moderately hard with good rigidity, low friction coefficient, and strong abrasion resistance.
- It exhibits good resistance to corrosion from chemicals, being relatively resistant to erosion and having strong chemical resistance.
- With tensile strength ranging from 50 MPa to 80 MPa, it demonstrates excellent tensile strength, toughness, and durability.
- Nylon 66 has a melting point of around 260°C, providing better heat resistance compared to Nylon 6.
Applications:
Automotive: Due to its excellent wear resistance, chemical resistance, and heat resistance, nylon is commonly used in the manufacturing of automotive engine components, body panels, doors, radiators, etc.
Textile Industry: Because of its excellent tensile strength, ease of molding, good elasticity, and strong abrasion resistance, nylon is often used to produce knitted fabrics, tire cords, sleeping bags, etc.
Industry: Due to its good abrasion resistance, nylon is frequently used in the production of gears, bearings, bushings, rollers, gaskets, etc.
Electronics and Electrical Appliances: Due to its good insulation properties, nylon is commonly used in the production of connectors, switches, housings, etc.
Nylon 11(PA11)
Properties:
- It has a low melting temperature and a wide processing temperature range, exhibiting good performance at low temperatures and maintaining good flexibility between -40°C to 120°C.
- With low water absorption, it can maintain dimensional stability in humid environments.
- The tensile strength ranges between 45 to 75 MPa, displaying good flexibility and elasticity, and it is not prone to fracture.
- It possesses excellent impact resistance and strong UV resistance capabilities.
Applications:
Automotive: With its chemical resistance and high impact resistance, nylon is commonly used in the manufacturing of automotive oil delivery pipes, brake system hoses, etc.
Sports Industry: Due to its excellent flexibility and impact resistance, nylon is used in sports equipment such as snowboards, ski boots, etc.
Medical Industry: Nylon 11’s good flexibility and biocompatibility make it suitable for surgical instruments, catheters, etc.
Industry: Because of its resistance to fuels, oils, and other chemicals, nylon can be used in the production of fittings, seals, etc.
Electronics and Electrical Appliances: With its good insulation properties, nylon can be used in connectors and cable insulation.
Nylon 12(PA12)
Properties:
- Similar to Nylon 11, but with lower density, melting point, and water absorption rate compared to Nylon 11.
- Relative density is low, at 1.02g/cm³, making it the smallest among the nylon series.
- Low melting point, ranging from 170 to 180°C, making it easy for molding with a wide processing temperature range.
- Low water absorption rate, providing good dimensional stability.
- Excellent impact resistance, high decomposition temperature, good low-temperature resistance, down to -70°C.
- It has excellent impact resistance and chemical stability, making it a good electrical insulator.
- It also possesses good toughness and elasticity.
Applications:
Automotive: Nylon 12 has excellent chemical resistance and high impact resistance, making it commonly used in automotive fuel lines, clutch lines, vacuum brake booster lines, etc. Due to its safety and reliability, it is an excellent lightweight material for automobiles.
3D Printing: Nylon 12 features high fluidity, low water absorption, moderate melting point, and fatigue resistance, gradually becoming an ideal material for 3D printing.
Medical: Nylon 12’s good flexibility, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility make it an excellent material for catheter production.
Household Goods: Nylon 12’s excellent fatigue resistance and suitability for use without coating make it suitable for eyeglass frames.
Nylon 46(PA46)
Properties:
- Nylon 46 has excellent tensile strength and high stiffness retention properties.
- With a melting point of approximately 295°C, it exhibits strong heat resistance.
- Its water absorption rate ranges between 1.5-2.5%, which is relatively low and allows it to maintain dimensional stability even in humid conditions.
- It possesses good chemical resistance, able to withstand corrosion from many chemicals.
Applications:
Automotive: Due to its excellent mechanical properties and chemical resistance, Nylon 46 is used to produce automotive engine and peripheral components such as cylinder heads, oil pan bases, transmissions, etc.
Electrical Industry: Because of its insulation and heat resistance, it is used in the production of contactors, coil frames, and other components in fields requiring high fatigue strength.
Consumer Goods: Nylon 46 is used to manufacture gears, bushings, and bearings for electrical appliances, sports equipment, and other products.
Nylon 610(PA610)
Properties:
- It has high tensile strength, falling between Nylon 6 and Nylon 66, with excellent abrasion resistance.
- It offers better heat resistance than PA11 and PA12, along with good UV resistance and chemical resistance.
- With relatively low hygroscopicity, it can maintain structural integrity in humid conditions and has good moldability.
Applications:
Automotive: Its outstanding high strength and heat resistance make it suitable for manufacturing engine covers, fuel tanks, radiator end tanks, etc.
Industry: Due to its high strength, abrasion resistance, and chemical stability, it is commonly used in the production of precision plastic components, bearings, liners, instrument housings, etc.
Sports: Because of its high strength and good abrasion resistance, it is used in the manufacturing of skateboards, snowboards, bicycle parts, etc.
Conclusion
This article mainly discusses six common types of nylon and their characteristics and applications. If you’re wondering which type of nylon is more suitable for manufacturing your parts, as a precision manufacturing company, DEK has a professional and experienced engineering team to provide services for you. Feel free to bring your part drawings for inquiries.
FAQs
How to process nylon sheet without deformation?
Immediately cooling the processed nylon parts in cold water helps to fix their shape. Additionally, a mixture of potassium acetate and water can be used to adjust moisture content, typically at a ratio of 1.25 to 1. These steps ensure stable shape after processing.
How to solve the problem of water absorption of nylon 6 and nylon 66?
Reduce water absorption to minimize the detrimental effects of moisture on its performance by applying surface hydrophobic modification materials to Nylon 6 and Nylon 66 plastics.
Which nylon is commonly used for injection molding?
Nylon 6 and Nylon 66 are commonly used nylon types for injection molding. They possess good mechanical strength, heat resistance, and abrasion resistance, making them suitable for manufacturing various parts and products.