CNC machining brass is a great option when you need high-quality, precise parts. Brass is easy to cut, gives a smooth finish, and doesn’t damage your tools quickly. That makes it a favorite material for machining.
In this guide, you’ll learn what CNC machining brass is, its advantages, the properties and types of brass, and a lot more. If you want to save time and get clean results, this guide will help you get there.
O que é a maquinagem CNC de latão?
CNC machining brass means using computer-controlled machines to cut, shape, and form brass parts. These machines are very accurate and can make detailed and complex parts with ease.
Brass is composed of copper and zinc. It’s popularly used in machining because it’s easy to work with, resists rust, and conducts electricity well.
Advantages of CNC Machining Brass Parts

There are many benefits of CNC machining brass, and some of these are the following:
High Precision & Accuracy
You program the machine with G-code, and it follows the code exactly. Your parts come out the same every time.
Easy to Machine
Brass cuts smoothly. You can make complex shapes faster, your tools last longer, and you spend less on production.
Rentável

Brass CNC machining delivers high-quality parts without a high price tag. You save money on materials and machine time.
Rust Resistance
Brass stands up to moisture and water without corroding. Your parts stay strong and last longer in a damp or wet environment.
Versatilidade
You can tweak the combination of copper and zinc to get different strengths, colors, or other traits. That means you can customize brass to your exact needs.
Good Conductivity
Brass moves heat and electricity well. If you need electrical connectors or heat-dissipating parts, use brass.
Fast Production

Máquinas CNC work quickly and run unattended. You get your parts sooner and can meet deadlines.
Nice Appearance
Brass has a warm, golden shine that looks great on visible parts. Your components can be both functional and attractive.
What Properties of Brass Make It Ideal for CNC Machining?
Brass has several properties that make it a great choice for CNC machining, and here are some of them:
| Imóveis | Latão |
| Ponto de fusão | 885 to 890 °C |
| Densidade | 8.5 g/cm³ |
| Módulo de elasticidade | 97 GPa |
| Condutividade térmica | 115 W/m·K |
| Resistividade eléctrica | 6.3 × 10⁻⁸ Ω·m |
Condutividade térmica

Brass contains copper, which is a good conductor. That’s why it is a good choice for electrical or heat-related applications.
You can also use EDM as part of the CNC machining process, as it works well with brass and helps you cut parts faster and more accurately.
Altamente maquinável
Brass is one of the easiest metals to machine. The lead in its alloy makes it more flexible and easier to cut.
Because it’s so machinable, you can get good results even if you’re still learning. That’s a big reason why many machinists choose brass for CNC projects.
Strength and Hardness
Even though brass is easy to machine, it’s still strong and durable. It might not be as strong as steel, but it holds up well and is tough enough for many jobs.
Some brass types include aluminum, which adds strength by forming a hard layer on the surface. You will need to use special tools like carbide cutters when machining this stronger type of brass.
Maleabilidade
Brass is easy to shape; that’s why it’s perfect for CNC machining. You can bend or form it into different shapes without cracking it.
Brass gets this quality mainly from the copper in it. The more copper a brass alloy has, the easier it is to shape. That’s why you’ll find brass useful when making custom parts with complex designs.
Common Types of Brass Alloys Used in CNC Machining
Below are the most commonly used types of brass alloys, as well as their advantages and disadvantages.
Latão C230

C230 is called the red brass because of its reddish color. It’s made of about 85% copper and 15% zinc. It’s softer than other types but still strong.
You’ll like using C230 if you need something that resists water and doesn’t rust easily. That’s why it’s often used in plumbing, roofing, jewelry, and decorations.
Prós:
- Doesn’t rust or corrode easily
- Easy to bend, shape, and join (soldering or brazing)
- Nice color for decorative parts
Contras:
- Not as easy to machine as C360
- Softer so it can get scratched or dented
Brass C260
C260 has a nice yellow color and is easy to shape, bend, and weld. It’s called cartridge brass because it’s often used to make ammunition shells.
This brass is great for hardware, plumbing, electrical parts, architectural work, and consumer products.
Prós
- Very ductile
- Resists corrosion well
- Easy to form and work with
Contras
- Doesn’t react well to acids like acetic, hydrochloric, or nitric
- Not good around ammonia or ammonia-based compounds
Latão C360

C360 is the most popular brass for CNC machining. It’s also called free-cutting or free-machining brass because it has about 3% lead, which makes it really easy to machine.
You’ll find it great for parts like screws, valves, fittings, fasteners, and joints, especially if you need to solder or braze them. It also holds up well under pressure and doesn’t crack easily.
Prós:
- Resists corrosion well
- Elevada resistência à tração
- Easy to shape and machine
Contras:
- Doesn’t hold up against acid
- The lead in it is not good for medical use
Surface Finishing Options for CNC-Machined Brass
Here are some of the common finishes you can choose for your machined brass parts:
Polishing: For a Shiny, Mirror-Like Look

Polishing is a great choice when you want your brass part to look really shiny, like a mirror. It’s perfect for parts that people will see, like musical instruments or decorative pieces. Aside from making your part look better, it also helps in protecting it from rust.
Brushing: For a Soft, Textured Look
Brushing gives your brass part a soft, even texture instead of a shiny look. It’s a good option when you want the part to look more subtle and less flashy. People often choose brushing for architectural designs where a clean, simple style is best.
Plating: For Stronger Protection and a New Look
Plating covers your brass part with another metal, like gold, silver, nickel, or chrome. It makes the part stronger and better at resisting rust and damage. Plating also changes how your part looks, depending on the metal you use.
Applications of CNC Brass Components
Many industries use CNC brass parts, such as the following:
Plumbing and Heating

You use brass to make parts like valves, fittings, and equipamentos because it resists rust and transfers heat well. Brass parts are strong and can handle tough conditions, so they are perfect for these jobs.
Automóvel
In the automotive industry, you use brass for things like radiator cores, sensors, and electrical connectors. Brass is easy to machine and very durable, which is important when you need precise parts that last a long time.
Electrical and Electronics
You can choose brass for making electrical parts such as connectors, switches, and terminals. It conducts electricity well, is easy to machine, and resists corrosion. Plus, brass looks good, so it’s great for high-end electronics too.
Marine Industry

If you build parts for boats or anything used in the ocean, you choose brass. Saltwater, humidity, and temperature changes can damage other metals, but brass stays strong and resists corrosion, so it is ideal for propellers, fittings, and fasteners.
What are the Factors to Consider for Custom Brass Parts?
There are many things you need to keep in mind when machining custom brass parts, and these are the following:
Material properties: Make sure the type of brass you choose matches what your project needs.
Production volume: CNC machining works for small or large orders. Think about the costs and choose the best option for your budget.
Tolerances and dimensions: CNC machines can make very precise parts. Check that the machine can meet the exact sizes you need.
Design complexity: CNC machining is great for making detailed and complicated parts. But make sure your design is not too difficult to manufacture.
Lead time: Think about how fast you need the parts. Check things like material availability, tooling, and how busy the production schedule is.
Conclusão
If you’re looking to create high-quality brass parts, DEK is ready to help. Our expert team specializes in CNC machining services, including milling, turning, drilling, and EDM. With years of experience working with different brass alloys, we know exactly how to handle your project, no matter how simple or complex it is.
At DEK, we are ISO 9001 certified, which means you can count on us for consistent, reliable results. Plus, we guarantee fast communication; you’ll always hear back from us within 12 hours. Contactar-nos today to get started!
FAQs about CNC Machining Brass
What is the tolerance range for brass?
The typical tolerance range for CNC-machined brass parts is ±0.005 mm, depending on the design and machining process.
Existe alguma desvantagem na maquinagem CNC de latão?
Yes, some types of brass are not suitable for medical or food-related applications due to potential toxicity. Also, brass is softer compared to steel, so it may scratch or dent more easily in some environments.
What is the lead time for machining brass?
At DEK, the typical lead time for machining brass parts is around 4-7 days, depending on the complexity and volume of the order.
When you need strong and light custom parts, you can opt for CNC machining aluminum. The properties of aluminum will tell you if it’s exactly what you need.
In this guide, I’ll help you understand how CNC machining aluminum works. You’ll learn why aluminum is a good material for your custom project.
O que é a maquinagem CNC de alumínio?
CNC machining aluminum means using computer-controlled machines to cut, shape, and make parts from aluminum material. With this process, you can create very detailed and complex designs that would be hard to do by hand.
CNC machines control everything carefully, so the custom aluminum parts you make are accurate and consistent. There are also special machines that can be set up just for working with aluminum’s unique properties.
Processo de maquinagem CNC de alumínio

Here are the CNC machining processes you can use for your custom aluminum parts:
Fresagem CNC
Fresagem CNC is a way to make custom aluminum machined parts by using a rotating cutting tool. The tool spins while the aluminum piece stays still. The machine removes material little by little in a very controlled way.
It can move in different directions to create complex shapes. With CNC milling, you can get very accurate and detailed parts.
Torneamento CNC
In CNC turning, the aluminum piece spins at high speed while a cutting tool stays in one place. The tool moves slowly against the spinning part to cut away material and shape it. CNC turning is perfect when you need round parts like tubes, rods, or rings.
Perfuração CNC

Perfuração CNC is used when you need to make holes in your aluminum machined parts. A drill bit spins and moves straight down into the material to create the hole. This method is great when your parts need to fit screws, bolts, or other pieces together.
Retificação CNC
CNC grinding is used when you need a very smooth and precise finish on your aluminum machined part. In this process, a spinning grinding wheel slowly removes tiny amounts of material from the surface.
It’s a great way to make parts very flat, very smooth, or to meet very tight size tolerances. You usually use CNC grinding as a final step after milling or turning.
Benefits of Aluminum that Make it Suitable for CNC Machining
Using aluminum for CNC machining has many advantages, and these are the following:
Resistência à corrosão

Aluminum naturally resists corrosion and scratching in normal air and marine environments. You can make it even more resistant by anodizing it.
Keep in mind that different grades of aluminum have different levels of corrosion resistance, but the ones most commonly used in CNC machining are very good at it.
Maquinabilidade
Aluminum is easy to cut, shape, and work with. Because it is soft and chips easily, you can machine it quickly without using a lot of power. It also costs less to machine than steel.
For you, this means faster production, lower costs, and more accurate parts. Aluminum doesn’t deform much during machining, so it’s easier to reach tight tolerances.
Low Temperature Performance
Most materials get brittle and weak at very cold temperatures, but not aluminum. It keeps its strength, softness, and flexibility even when it’s freezing. This makes it a good choice if your parts need to work in very cold environments.
Relação força/peso

Aluminum is about three times lighter than steel, but it’s still very strong. This strong yet lightweight quality is called the strength-to-weight ratio.
Because of this, you can use aluminum for parts that need to be strong without being heavy, like in cars, airplanes, and other high-performance products.
Reciclabilidade
CNC machining creates a lot of leftover chips and waste. Luckily, aluminum is highly recyclable. It doesn’t take much energy, time, or money to recycle aluminum, which can help save costs and reduce waste. Plus, using recyclable materials like aluminum is better for the environment.
Condutividade eléctrica
Pure aluminum conducts electricity very well. Even though aluminum alloys conduct a little less, they are still good enough for making electrical parts. But if you need a part where conductivity is a problem, aluminum might not be the right material.
What Types of Aluminum are Used in CNC Machining?
There are different types of aluminum that are commonly used in CNC machining, and some of these are the following:
| Liga de alumínio | Composição | UTS (MPa) | Densidade (g/cm³) | Specific Strength (kN·m/kg) |
| 7075-T651 | AlZn5.5MgCu | 490 | 2.81 | 170 |
| 2024-T351 | AlCu4Mg1 | 430 | 2.79 | 150 |
| 6082-T651 | AlSi1MgMn | 310 | 2.68 | 120 |
| 6061-T6 | AlMg1SiCu | 310 | 2.7 | 115 |
| 5052-H32 | AlMg2.5 | 260 | 2.68 | 97 |
Alumínio 6061

You can use 6061 aluminum for many things, like manufacturing, building, making consumer products, and even in airplanes. It’s very versatile and easy to weld.
This aluminum is medium-strong, can be heat-treated, and resists rust very well. You’ll find it easy to machine and work with, especially when it’s softened/annealed.
Alumínio 7075
If you need very strong aluminum, you should choose 7075 aluminum. It’s one of the strongest types you can get. It also holds up well under repeated stress, which is why it is perfect for parts that go through a lot of pressure.
Alumínio 7075 is very popular in the aerospace industry, where parts need to be both strong and complex.
Alumínio 5052
You should use 5052 aluminum when you need something that bends easily without cracking. It’s very good at resisting rust, especially from saltwater, so it’s great for marine uses.
You can’t heat treat it to make it stronger, but it’s still a strong and flexible aluminum that’s easy to work with.
Alumínio 2024

If you need aluminum that’s strong and handles stress well, 2024 is also a good choice. It’s often used in airplanes and vehicles because it is tough.
But you should know that it doesn’t resist corrosion as well as other types, so it usually needs a protective coating.
Alumínio 6082
When you want a strong and tough aluminum that’s still easy to machine and weld, you can use 6082 aluminum. It’s great for building structures like bridges and towers.
It resists corrosion well and is often used when you need strength and good durability together.
Surface Finishes for CNC Aluminum Parts
After you finish machining an aluminum part, you can do a few extra processes to make it look better, work better, and last longer. Here are the most common ones:
Revestimento

You can coat the aluminum part with another material, like zinc, nickel, or chrome. This makes the part stronger and protects it. Usually, you do this using an electrochemical process.
Another way to protect and color a part is by powder coating. You spray a dry colored powder onto the part using an electrostatic spray gun. Then you heat the part to about 200°C so the powder melts and sticks.
Jateamento de esferas
If you want a nice-looking finish, you can try bead blasting. In this process, you blast tiny glass beads at the part using a high-pressure air gun. This smooths the surface and gives a satin or matte look.
The main things you control are the size of the beads and the air pressure. Only use bead blasting if the exact size of your part is not super important, because it can change the dimensions a little.
Anodização
If you want to make the surface harder and non-reactive, you can anodize the part. In anodizing, you dip the part into a diluted sulfuric acid solution and run electricity through it. This creates a tough aluminum oxide layer on the surface.
How thick and strong the layer gets depends on the solution, how long you anodize it, and the amount of electricity used. You can also anodize parts to add color.
Tratamento térmico
If your part is made from a heat-treatable aluminum alloy, you can heat-treat it to make it stronger and improve its mechanical properties.
Applications of Aluminum Machined Parts in Industry

Below are some of the industries that commonly use aluminum machined parts:
Aeroespacial
Aluminum CNC machined parts are strong, so they are perfect for making aerospace structural parts like engine components, airframes, and landing gear.
Since aluminum is lightweight, it reduces the weight of airplanes. CNC machined aluminum parts are also important for building parts like wing panels and fuselage sections.
Automóvel
In the automotive industry, CNC machined aluminum parts are used in engine components, suspension systems, transmission housing, and electric vehicle parts. Aluminum’s strength, durability, and light weight help reduce the overall weight of vehicles and improve their durability.
Eletrónica de consumo
Aluminum CNC machined parts are widely used in consumer electronics like laptops, smartphones, tablets, and audio equipment. Aluminum is ideal for making device casings because it is lightweight and provides protection for internal components.
High-end audio equipment such as amplifiers, headphones, and speaker enclosures often uses aluminum parts because it helps reduce vibrations and dissipates heat effectively.
What are Some Design Tips for Aluminum CNC Machining?

Here are some design tips to make sure your aluminum part is both functional and easy to make:
- Deep cavities can be hard to machine and may cause tool damage. Keep deep features to a minimum or split them into multiple steps for easier machining.
- Keeping the wall thickness uniform helps avoid wasting material or causing distortions. Too much variation can create weak spots or uneven stress.
- Sharp internal corners are hard to machine. Adding rounded edges helps make smoother cuts and reduces stress.
- Ensure that the cutting tool can access all parts of the design. Think about tool size and shape when designing features like holes or slots, so the tool doesn’t get blocked.
- Very thin walls can vibrate during machining and affect surface quality. Stick to a reasonable thickness for strength and stability.
- When adding threads to aluminum, make space at the bottom of the threads so the cutting tool can exit cleanly and produce high-quality threads.
- If your parts will have additional finishes like anodizing or bead blasting, make sure your design accounts for the extra material that may be removed or added during these steps.
Conclusão
Now you know how CNC machining aluminum works and why it’s a good choice for many custom parts. You also understand the benefits of aluminum and how to design better parts of it.
At DEK, we can help you create strong, lightweight, and high-quality custom aluminum machined parts. Contactar-nos now to get fast, reliable CNC machining services for your project.
FAQs
How much does CNC machining aluminum cost?
The cost of CNC machining aluminum depends on factors like the type of aluminum, part complexity, and order size. Larger orders often reduce the cost per part by spreading setup and tooling expenses over more units.
Quais são as alternativas ao alumínio na maquinagem CNC?
If aluminum is not suitable for your project, you might consider other materials. Steel offers high strength but is heavier and more challenging to machine. Stainless steel provides excellent corrosion resistance.
Brass is easy to machine and has good corrosion resistance. Plastics like ABS or Delrin are lightweight and cost-effective for non-structural parts.
What factors should be considered when machining aluminum?
When machining aluminum, you should pick the right alloy for strength and corrosion resistance, use tools with sharp angles for easy cutting, and set the cutting speed and feed rate correctly to avoid tool wear.
Always use coolant to keep things cool and protect the tools, make sure chips are cleared away properly, and remember that aluminum can expand with heat, so plan for tight tolerances carefully.
When you make medical parts, you need to be very exact because a small mistake can cause serious problems. That’s why it’s important to know how to achieve precision in medical parts.
In this guide, you’ll learn what precision machining is and how you can make sure every part you make is accurate, safe, and ready to use for the medical industry.
What is Precision Machining?
Precision machining means making parts that are almost exactly the same size with little difference. You do this by using machines controlled by computers, like CNC machines or lasers. You also want the parts to match the original design exactly.
The Role of Precision in Medical Parts Manufacturing
As medical care improves, the need for precise devices grows to help people stay healthy. Since these devices affect health, every part must be made with great care. They must work perfectly, especially inside the body, where mistakes can be serious.
To achieve this, you can use different precision machining processes that we will discuss further below.
Benefits of Precision Machining in the Medical Industry
You can get a lot of benefits when you use precision machining in the medical industry, and some are discussed below.
Make Precise Devices
With precision machining, you can create medical devices that are very accurate. Tools like 5-axis milling and EDM allow for detailed and smooth parts, even with tough materials.
Make Devices from Different Materials
Precision machining lets you use strong materials like surgical steel and titanium, which meet FDA safety standards. These materials are used in things like implants and surgical tools.
Make Smaller Devices
Precision machining helps create smaller devices like insulin pumps and pacemakers. These devices are comfortable and don’t get in the way, so it is easier for people to live their daily lives.
Tools and Technologies Used in Precision Machining

Precision machining in making medical components uses different tools and technologies, such as:
Máquinas CNC: These machines are controlled by computer programs to ensure precise and repeatable machining for you.
CAD/CAM Software: This software helps you design medical components and generate instructions for the machining process.
Advanced Cutting Tools: Tools made of carbide, ceramic, and high-speed steel are used to get the precision and quality you need for medical components.
High-Speed Machining (HSM): This technology speeds up machining. It makes the process more efficient and improves your productivity.
Multi-Axis Machining Centers: These machines can perform complex operations from different angles. They can help you create detailed medical parts.
Metrology Equipment: Tools like coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and laser trackers check the accuracy and quality of the components you make.
Precision Machining Processes for Medical Component Manufacturing

Here are some of the precision machining processes that you can use:
Maquinação CNC
This method uses computers to control machines. It makes parts precise and consistent every time.
5-Axis Milling
The advanced technique lets you create complex shapes in one setup, reducing mistakes and saving you time.
Maquinação por Descarga Eléctrica (EDM)
This is used for hard materials like titanium and tungsten. It uses electrical discharge to shape the material. It makes highly detailed and precise parts.
Importance of Quality Control in Precision Machining for Medical Industry

Below are the main reasons why it’s so important:
- Ensure every part is made exactly right for patient and user safety.
- Regular quality control leads to parts that are less likely to fail.
- Catch problems early to avoid costly fixes and delays.
- Follow industry rules to maintain safety and quality standards.
Challenges for Precision Medical Machining
In medical machining, you need to avoid contamination, keep up with new tech, and manage high costs. Below are some of the other challenges you might encounter and how to solve them.
Working with Titanium

Titânio is a hard material, so it is often used because it’s strong and lasts a long time. You might use it to make biopsy tubes or surgical scissors. These tools help doctors collect tissue samples or perform surgeries.
But titanium is hard to work with, so you must use special tools and make the machining speed slower if needed.
Making Complex Parts with CNC
The human body is complicated, and medical tools need to match that. Use 5-axis CNC machines for detailed, multi-angle cuts. Use software to simulate the process before cutting real material.
Handling Tight Tolerances
When you make medical parts with CNC machines, you often deal with very tight tolerances. Use high-precision machines and inspection tools. Run regular quality checks to catch problems early.
Small Batch Orders
A small batch order usually means fewer than ten parts. You can make these small batches with CNC machines or 3D printers.
Applications of Precision in Medical Parts
Now, here are some examples of medical parts that need precision machining:
Dispositivos implantáveis

When you’re working with pacemakers, stents, or bone implants, you need tiny, precise parts made from safe materials like titanium.
Equipamento de diagnóstico
You use precision-machined parts in MRI machines, CT scanners, and ultrasound devices. These parts help you get clear, high-resolution images, which are important for making the right diagnosis.
Instrumentos cirúrgicos
You use precision machining to make sharp tools like scissors, forceps, and other surgical instruments. This process helps you get clean edges without rough spots, so your tools are safe and work well during surgery.
Endoscopic Tools
You count on flexible, detailed tools to look inside the body. Precision machining helps you build parts that move easily and work exactly as needed during challenging procedures.
Aparelhos auditivos
For hearing aids, you need tiny, detailed parts. Precision machining lets you create these small pieces and circuits with the accuracy and size needed to keep the devices light, comfortable, and effective.
Respiratory Equipment
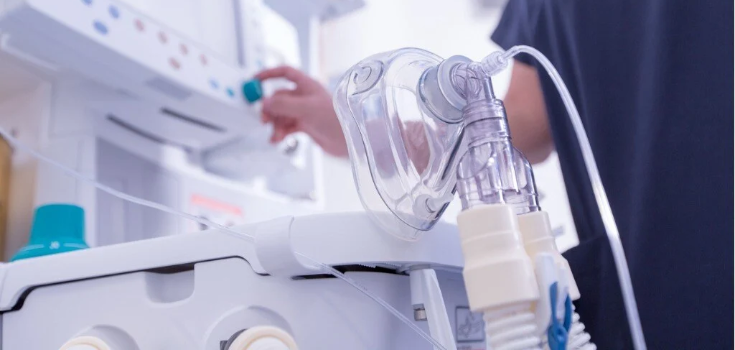
You use precision-machined parts in ventilators and other breathing devices. These parts must work perfectly, especially in emergencies.
Precision Machining for Medical Devices From DEK
DEK offers precision machining for medical devices. We use various tools and methods, like CNC and EDM machining, laser cutting, laser welding, and additive manufacturing. We also handle sheet metal fabrication and other finishing services.
We can give you different options, so you get what works best for your needs. Contactar-nos to talk about your next medical device project or get a free quote.
Conclusão
Precision machining is important for improving medical technology. It helps make tiny, accurate parts needed for advanced medical devices. This process makes sure the parts are lightweight, strong, and work well.
If you work with waterjet cutting, you know how important the nozzle is. It directs the high-pressure water stream to cut through materials accurately. Choosing the right nozzle affects cutting speed, precision, and durability.
In this guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know about waterjet cutting nozzles.
What are Waterjet Cutting Nozzles?
A waterjet nozzle is the part of a waterjet machine that directs the water stream to cut a material. It is also called a focusing tube or mixing tube. The nozzle is very strong because it needs to handle high-pressure water.
Over time, the nozzle wears out due to the pressure, so you need to replace it regularly.
What is the Purpose of the Water Jet Nozzle?

The main job of the waterjet nozzle is to focus the water stream for precise cutting. The size of the water stream depends on the material and its thickness.
Inside the nozzle, there is a jewel orifice, which controls the water flow. This helps the nozzle last longer and improves cutting accuracy.
Key Components of a Waterjet Cutting Nozzle
Waterjet nozzles have three main parts: the jewel orifice, the mixing tube, and the focusing tube. Each part helps the waterjet cut materials accurately and efficiently.
The jewel orifice, usually made of sapphire or diamond, pushes high-pressure water into the mixing tube. Here, the water mixes with abrasive materials. Then, the mixture moves through the focusing tube to make precise cuts.
Using high-quality parts makes the nozzle last longer and work better over time.
How Waterjet Nozzles Work?

Waterjet cutting nozzles convert high-pressure water into a fast-moving stream. When mixed with abrasives, this stream can cut through tough materials like metal and ceramics. This makes water jet operation useful for many industrial and manufacturing applications.
The nozzle controls the speed and precision of the cut. A smaller nozzle creates detailed cuts, while a larger one increases cutting speed for bigger projects. It also focuses the water stream, turning pressure into cutting power
Waterjets can cut almost any material, including glass, marble, wood, and even food. They can drill titanium, make fine details in stone and metal, and sterilize liquids. Each material and thickness requires the right nozzle size to get the best results.
Types Of Waterjet Cutting Nozzles
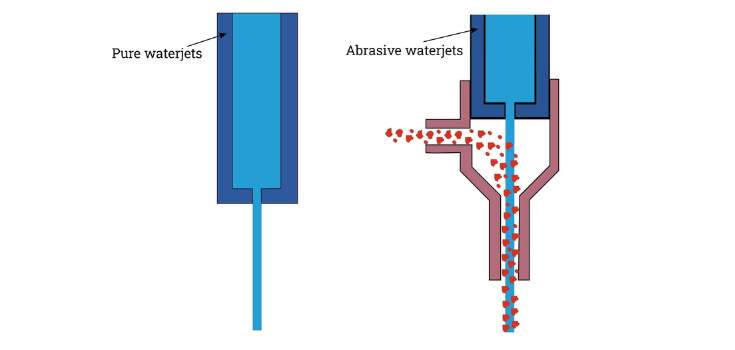
Here are the two types of waterjet nozzles:
1. Pure Waterjet Nozzles
- Uses only water (no abrasives).
- Cuts soft materials like paper, foam, rubber, textiles, cardboard, and plastics.
- Has a very small opening because no abrasive particles are used.
2. Abrasive Waterjet Nozzles
- Uses water and abrasive particles to cut harder materials.
- Has a special mixing chamber where abrasive particles are added to the water.
- The high-pressure water speeds up the abrasive particles to cut materials like metal, ceramics, stone, glass, and composites.
Specifications of a Water Jet Nozzle

A water jet nozzle has different features that affect how it works. Here are the main things you need to know:
Orifice Diameter
The orifice diameter is the size of the hole in the nozzle where water comes out. A smaller hole creates a stronger water jet but also wears out the nozzle faster. The diameter of the water jet cutting nozzle is usually three times the orifice diameter. A small orifice helps with accuracy, but if it is too small, it slows down cutting and wears out quickly.
Flow Rate
The flow rate is how much water passes through the nozzle in a certain time. It is measured in liters per minute (LPM) or gallons per minute (GPM). A higher flow rate makes cutting faster but also causes more wear on the nozzle.
Nozzle Size
The nozzle size is the width of the bore hole, usually three times the orifice diameter. There are three types of nozzle sizes. Small nozzles, which range from 0.254 mm to 1.016 mm (0.01 in to 0.04 in), are used for precise and detailed cutting.
Medium nozzles, which range from 1.016 mm to 2.032 mm (0.04 in to 0.08 in), are used for general cutting where high accuracy is not needed. Large nozzles, which range from 2.032 mm to 6.35 mm (0.08 in to 0.25 in), are used for fast cutting of large materials.
Pressure Rating
The pressure rating tells you the highest amount of water pressure a nozzle can handle properly. If the pressure goes beyond this limit, the nozzle can get damaged or even break. Different nozzles have different pressure ratings, and manufacturers provide this information when you buy a replacement nozzle.
A modern waterjet cutting nozzle can reach pressures as high as 90,000 psi. But at such high pressure, the nozzle and other parts wear out quickly. The best pressure for long-lasting performance is between 40,000 psi and 60,000 psi.
Material Used For Making Waterjet Nozzles
Waterjet nozzles come in different materials, depending on how long they need to last, how much pressure they can handle, and their cost. Here are the most common materials:
Carboneto de tungsténio

Carboneto de tungsténio is the most popular choice. It is very strong—almost as hard as diamond. These nozzles work well under very high pressure (up to 90,000 psi). If you use them properly, they can last over 200 hours. If used roughly, they may need to be replaced after 100 hours.
Diamante
Diamond nozzles are the hardest and most durable. They can handle extreme pressure and cut the toughest materials. These nozzles can last up to 1,000 hours. However, they are the most expensive, costing about 20 times more than sapphire nozzles. If you do a lot of heavy cutting, diamond nozzles may be the best choice.
Sapphire
Sapphire nozzles are strong and affordable. They do not react with chemicals. However, they have a shorter lifespan, usually between 50 to 100 hours. They can handle water pressures between 60,000 and 70,000 psi. Ruby nozzles are very similar to sapphire nozzles.
Cerâmica
Ceramic nozzles are a newer option. They can be even stronger than hardened steel and are resistant to rust and corrosion. Their lifespan depends on the type of ceramic used.
What Materials Can a Waterjet Nozzle Cut?

A waterjet nozzle can cut almost any material. Here are some common ones:
Metais: You can cut even the hardest metals, like hardened steel. For a smooth and fast cut, you’ll need an abrasive jet nozzle.
Plásticos: You can cut any plastic without melting it. Most plastics need an abrasive jet nozzle.
Cerâmica: Waterjets are often used to cut ceramic tiles and stone. Depending on the ceramic type, you may use either an abrasive or a pure waterjet nozzle.
Rubber: A pure waterjet nozzle at low pressure is perfect for cutting rubber. This method is cost-effective.
Glass: You can cut glass for art, construction, and decoration. An abrasive jet nozzle can even cut bulletproof glass.
Thin Films: You can cut thin foils, like aluminum foil, using a pure waterjet nozzle. Even thin metal foils can be cut this way.
Foam: Waterjet cutting gives clean cuts on foam without burn marks. A pure waterjet nozzle works well and is affordable.
Wood: Soft or thin wood can be cut with a pure waterjet nozzle. For thick or hardwood, you’ll need an abrasive jet nozzle.
Nozzle Connection Type
When choosing a waterjet cutting nozzle, you have different ways to connect it. Here are three common types:
Threaded Nozzles

Threaded nozzles have screw-like threads on the ends. You need special tools to attach and remove them, but they provide a very secure fit. These nozzles can handle extremely high pressure without leaking. Once properly installed, you don’t have to worry about them disconnecting by accident.
Quick-Connect Screw Nozzles
Quick-connect screw nozzles are a mix of snap and threaded nozzles. They have a locking system like snap nozzles but also require some screwing to secure them in place. This makes them more reliable than snap nozzles, as they are less likely to disconnect accidentally. At the same time, they are still easier to use than fully threaded nozzles.
Quick-Connect Snap Nozzles
Quick-connect snap nozzles, also called quick-disconnect nozzles, do not require any tools to attach or remove. They use a snap-lock system to stay in place, and they are very easy to use. However, they are not as strong as threaded nozzles and may not handle very high pressure. In some cases, the locking mechanism can accidentally release during operation.
How to Choose the Right Waterjet Nozzle?

Choosing the right waterjet nozzle depends on a few key factors:
- Think about what you need the nozzle for. Some jobs limit your options. For high pressure, avoid snap connection nozzles.
- Nozzles wear out at different rates. If using abrasives, pick a tough material. Diamond lasts the longest but costs more. Tungsten carbide is a solid, common choice.
- The hole size affects cutting. There’s no one-size-fits-all, so check the manufacturer’s guide or test different sizes.
- Choose a nozzle that can handle more pressure than your system uses for safety and durability.
- Use a machinability chart to match the right nozzle to your material. This improves cutting and extends nozzle life.
Applications of Waterjet Cutting Nozzles
Here are some key areas where you might see them in action:
Indústria aeroespacial

If you’re working in aerospace, you need precise cuts for strong but lightweight materials like titanium, aluminum, and composites. Waterjet nozzles help you create complex parts, such as aircraft panels and engine components, without weakening them.
Indústria automóvel
In the automotive world, waterjet nozzles let you cut metal, rubber, and composite materials quickly and accurately. Whether you’re making engine parts, car body pieces, or custom modifications, waterjet cutting is a great way to get clean, precise results.
Indústria eletrónica
If you work with electronics, you know how delicate materials like circuit boards and semiconductor wafers can be. Waterjet nozzles allow you to cut these fragile components without causing damage. They also help in making connectors, housings, and other small electronic parts with tight tolerances.
Medical Devices Industry

Waterjet cutting is essential for making medical devices like surgical tools, implants, and diagnostic equipment. Since it can cut materials like stainless steel, titanium, and ceramics without heat, you don’t have to worry about damaging delicate medical parts.
Effects of Water Quality on Nozzle Lifespan
The quality of water you use directly affects how well your waterjet nozzles work and how long they last. Dirty water with impurities can wear down the nozzles, so it can make the cutting process less effective. Using clean, high-quality water helps keep your nozzles working properly for a longer time.
Filtering your water or using a water treatment system can greatly reduce the damage caused by impurities, helping your nozzles last longer. Paying attention to water quality ensures your cutting system works consistently and reliably. By taking care of the water you use, you improve the efficiency and performance of your waterjet cutting.
Tools for Monitoring Nozzle Lifespan
To keep your waterjet cutting nozzles working well and lasting longer, you need to check their condition regularly. There are several tools that help you catch problems early, saving you time and money on unnecessary repairs.
Here are some useful tools for monitoring nozzle performance:
Wear Monitoring Sensors
Wear monitoring sensors track changes in the nozzle’s size or performance over time. They provide real-time data, helping you detect early signs of damage. By catching these issues early, you can schedule maintenance before the nozzle fails, reducing unexpected downtime.
Laser Alignment Systems
Laser alignment systems make sure the nozzle is positioned correctly. Proper alignment ensures clean, precise cuts and even wear on the nozzle. If the nozzle is misaligned, it can cause uneven cutting and wear out faster. Using a laser alignment tool regularly helps maintain accuracy and extend nozzle life.
Pressure Gauges

Pressure gauges measure the water pressure in the system. Keeping the pressure steady ensures the nozzle works properly. If the pressure suddenly drops or spikes, it could mean the nozzle is wearing out or getting clogged. Monitoring pressure helps you spot issues before they affect cutting quality.
Inspection Cameras
Inspection cameras let you take a close look at the nozzle without taking the system apart. You can check for cracks, wear, or erosion quickly and easily. Regular inspections with a camera help you catch problems early and keep your nozzles in good shape.
Flow Rate Meters
Flow rate meters check how much water and abrasive material are moving through the nozzle. If the flow rate changes, it could mean there’s a clog or the nozzle is wearing down. These meters help ensure smooth operation and prevent buildup inside the nozzle.
Common Problems of Waterjet Cutting Nozzles
Waterjet cutting nozzles are tough, but they can develop problems over time. Knowing what to watch for and fixing issues early will keep your cuts clean and your nozzle working longer. Here are some common problems and how to solve them:
Clogging Issues

Dirt, abrasive particles, or leftover materials can clog the nozzle, blocking water flow and making cuts less precise.
Clean the nozzle regularly with high-pressure air or water. Use a good filtration system to prevent clogs in the first place.
Sobreaquecimento
Running the system too long without breaks, using too much pressure, or poor maintenance can cause the nozzle to overheat, reducing efficiency.
Keep the system well-ventilated. Take breaks during long cuts and monitor pressure levels to avoid overheating.
Uneven Cuts
If your cuts look rough or uneven, the nozzle might be misaligned, parts may be worn out, or the water and abrasive flow may be inconsistent.
Check that the nozzle is aligned correctly. Make sure water pressure and abrasive flow are steady. Replace worn parts like focusing tubes or orifices when needed.
Leaks

Leaks can happen at connection points due to worn-out seals or damage, reducing cutting power and wasting water.
Check the nozzle and fittings for wear or loose connections. Tighten or replace seals as needed.
Excessive Wear
Nozzles wear down over time from constant high-pressure water and abrasives. This can make your cuts less accurate.
Inspect your nozzle often and replace worn-out parts. Use high-quality abrasives and adjust pressure settings to slow down wear.
Conclusão
Keeping your waterjet cutting nozzles in top condition is important to achieving precise, high-quality cuts. By choosing the right nozzle, monitoring wear, and maintaining clean water, you can extend the lifespan of your equipment and improve efficiency.
Em DEK, we manufacture precision components using advanced waterjet cutting machines. If you need high-quality nozzles or custom-cut parts, contact us today to see how we can support your production needs!
FAQs
How are waterjet cutting nozzles made?
Waterjet cutting nozzles are made from tungsten carbide, a hard but brittle material. They are formed by pressing powdered tungsten carbide into a mold and heating it under high pressure.
What is a water jet cutting nozzle’s diameter?
The size of a water jet cutting nozzle depends on the type of cutting you’re doing. For abrasive waterjet cutting, the water stream is round and usually between 0.030” and 0.040” (0.76 mm and 1.02 mm) wide. Because of its round shape, it’s hard to cut perfectly square inner corners—the jet will always leave a small curve.
How long does a waterjet nozzle last?
You should replace your waterjet nozzle after 40 to 1000 hours of use. The lifespan depends on what you’re cutting, water pressure, abrasive quality, and nozzle material. Check it regularly to catch wear early and keep your cuts precise.
What is the cost of waterjet cutting nozzles?
Waterjet cutting nozzles cost between $20 and $400+, but the price doesn’t always mean better value. A $400 diamond nozzle may save you money by lasting longer than a $20 sapphire one. Tungsten carbide nozzles ($50-$100) offer a good balance of cost and durability.
How do you know when it’s time to get a new waterjet nozzle?
Replace your nozzle if cutting is less precise, abrasive use increases, or the machine slows down. Check for wear regularly to avoid downtime and keep your waterjet running smoothly.
What factors describe the lifespan of waterjet cutting nozzles?
Your waterjet nozzle lasts longer if you use clean water, high-quality abrasives, and the right cutting pressure. Heavy use wears it out faster. To extend its life, maintain proper pressure, use good abrasives, and follow best practices.
Poderá estar a perguntar-se: o latão enferruja? É uma boa pergunta porque a ferrugem pode causar grandes problemas a muitos metais, especialmente ao ferro e ao aço.
Neste guia, ficará a saber o que acontece ao latão ao longo do tempo e como reage a diferentes condições.
O que é o latão?
O latão é uma liga composta maioritariamente por cobre e zinco. Normalmente, tem cerca de 60-70% de cobre e 30-40% de zinco. A alteração destas quantidades altera a força, a flexibilidade e a resistência à corrosão do latão. Por vezes, são adicionados outros metais como chumbo, estanho ou alumínio.
O latão enferruja?
Não, o latão não enferruja porque não tem ferro. A ferrugem só acontece em metais com ferro. Mas o latão pode corroer-se em condições difíceis
Uma alteração comum é o embaciamento, que faz com que a superfície pareça baça por causa de uma camada chamada pátina. A pátina é esverdeada e feita de compostos de cobre. Em locais muito agressivos, o latão pode perder zinco, um processo chamado dezincificação, o que pode enfraquecê-lo.
Propriedades de ferrugem do latão vs. composição da liga
Estas partes do latão alteram o seu comportamento:
Zinco: Adiciona-se zinco para tornar o latão mais forte e mais flexível. Mas se houver demasiado zinco, o latão pode perder zinco em condições difíceis, o que pode causar danos. Os latões com menos zinco, como o latão naval e o latão estanhado, resistem melhor à ferrugem.
Cobre: Mais cobre significa melhor proteção contra a ferrugem. O cobre reage com a água e o ar para formar uma camada fina que protege o latão por baixo. Os latões vermelhos têm cerca de 80% de cobre e resistem melhor à ferrugem do que os latões amarelos, que têm 60-70% de cobre.
Outros metais: A adição de estanho ajuda a impedir a perda de zinco e protege o latão da ferrugem. O chumbo torna-o mais fácil de moldar e maquinar. O alumínio torna o latão mais forte e mais resistente à ferrugem.
Comparação da oxidação do latão com a oxidação do latão e com a mancha do latão
Vamos comparar a ferrugem do latão com a oxidação e a mancha para os compreender melhor.
Oxidação do latão

O latão tem cobre nele. Quando o deixamos ao ar e à humidade, o cobre reage e forma uma camada fina chamada óxido de cobre. Esta camada protege o latão. Poderá ver a cor mudar, por vezes tornando-se verde com o passar do tempo (a chamada pátina).
Ferrugem do latão
O latão não enferruja. A ferrugem só acontece quando o ferro reage com o ar e a humidade. Uma vez que o latão não tem ferro (é feito de cobre e zinco), não tem de se preocupar com a ferrugem.
Latão manchado
A mancha acontece quando o cobre do latão reage com o enxofre no ar. Isto cria uma camada escura na superfície. Mas não se preocupe, pode limpá-la e devolver-lhe o brilho.
Normas-chave para a resistência à corrosão do latão

Eis o que precisa de saber sobre as principais normas que ajudam a verificar a resistência do latão à corrosão:
Normas ASTM (dos EUA)
O Sociedade Americana de Ensaios e Materiais (ASTM) tem algumas regras que o ajudam a testar o latão e a verificar a sua resistência à corrosão.
ASTM B887: Isto diz-lhe que tipo de latão é bom para resistir à dezincificação (um tipo de corrosão). Também explica de que material deve ser feito o latão e qual a sua resistência.
ASTM B858: Isto mostra como testar o latão, colocando-o numa solução química para ver se resiste à dezincificação.
Normas ISO (das Diretrizes Internacionais)
A Organização Internacional de Normalização (ISO) também lhe dá passos claros para testar o latão e certificar-se de que cumpre as normas de qualidade.
ISO 6509: Este teste verifica se o latão resiste à dezincificação. Coloca-se o latão numa solução de cloreto de cobre e verifica-se a profundidade da corrosão.
ISO 18086: Esta norma abrange todas as ligas de cobre (como o latão) e garante que necessitam de determinados níveis de desempenho e de resistência à corrosão.
Tipos de corrosão que o latão pode enfrentar

Aqui está uma tabela simples que o pode ajudar a compreender os tipos de corrosão que o latão pode sofrer.
| Tipo de corrosão | O que acontece |
| Manchamento | O latão pode ter um aspeto baço ou descolorido. Isto acontece apenas na superfície e é fácil de limpar. |
| Dezincificação | Em locais salgados ou com muito cloro, o latão pode perder zinco e tornar-se fraco e poroso. |
| Fratura por corrosão sob tensão | Se o latão estiver sob tensão e exposto a determinados produtos químicos, pode rachar ou partir. |
| Corrosão galvânica | Se o latão entrar em contacto com um metal mais nobre numa área húmida, pode corroer mais rapidamente. |
| Corrosão por pite | Pequenos furos ou buracos podem aparecer na superfície do latão em condições muito duras. |
Factores que afectam a corrosão e a ferrugem do latão
Seguem-se alguns dos factores que podem afetar a forma como o latão se corrói ou enferruja:
Composição do latão
Se o latão tiver muito cobre, resiste melhor à corrosão. Mas se tiver demasiado zinco, pode perder zinco com o tempo (isto chama-se dezincificação). A adição de elementos como estanho, silício ou alumínio ajuda a protegê-lo da corrosão.
Condições ambientais

Se o latão for molhado com frequência, corrói-se mais rapidamente (mas não enferruja como o ferro). A água salgada pode extrair o zinco do latão. Os locais ácidos também fazem com que o latão se corroa rapidamente.
Exposição a produtos químicos
Estar perto de enxofre pode fazer com que o latão fique manchado devido à formação de sulfureto de cobre. O amoníaco é ainda pior - pode causar fissuras no latão que está sob pressão ou stress.
Temperaturas elevadas
Se utilizar latão em locais muito quentes, este irá corroer-se mais rapidamente, especialmente em ambientes difíceis.
Tensões mecânicas
Se o latão estiver dobrado, esticado ou sob pressão, pode rachar mais facilmente devido ao stress e à corrosão.
Revestimentos de proteção

Se revestir o latão com algo que o proteja, este não se corroerá tão rapidamente.
Aplicações do latão devido às propriedades de resistência à ferrugem
Eis algumas formas comuns de utilização do latão na vida quotidiana:
Acessórios de canalização: O latão pode ser utilizado em canos de água, bombas, torneiras e peças de barcos. Não enferruja, pelo que dura muito tempo perto da água.
Conectores eléctricos: O latão funciona bem para fichas, tomadas e fios. Deixa a eletricidade fluir e não enferruja nem se parte facilmente, pelo que é ótimo para coisas como peças de interruptores e pinos eléctricos.
Instrumentos musicais: O latão é perfeito para fazer instrumentos como trompetes, trombones e tubas. Soa muito bem e é fácil de moldar.

Decorações em estruturas arquitectónicas: O latão pode ser utilizado em artigos de luxo, como candeeiros, grades e puxadores de portas. Tem bom aspeto e não se desgasta facilmente, pelo que também é utilizado na construção de peças que têm de durar e ter bom aspeto.
Peças para automóveis: O latão é utilizado nos radiadores e aquecedores dos automóveis, uma vez que movimenta bem o calor e não é danificado pelos líquidos de refrigeração.
Rolamentos e buchas: Se precisar de peças que se movam suavemente e durem em locais difíceis, o latão é uma boa escolha. É utilizado em máquinas para peças de baixa fricção. Também é utilizado em luvas feitas para trabalhar em locais enferrujados ou cheios de químicos.
Moedas resistentes à ferrugem: Algumas moedas são feitas de latão porque não enferruja, é forte e fácil de prensar.
Armas: O latão pode ser utilizado para fabricar ferramentas que não produzem faíscas, o que é importante em locais com materiais inflamáveis, como fábricas de produtos químicos. Também é utilizado para invólucros de balas porque não enferruja, é forte e fácil de trabalhar.
Métodos de prevenção e tratamento da corrosão do latão
Seguem-se algumas dicas simples para o ajudar a proteger e a cuidar dos seus artigos de latão.
Prevenir a corrosão do latão

- Escolha ligas de latão com níquel, crómio ou latão DZR para resistir à corrosão.
- Aplique zinco, níquel ou cromagem, ou utilize vernizes transparentes e nano-revestimentos para bloquear a humidade e o ar.
- Aplicar tratamentos anti-manchas para criar uma camada protetora que impeça as manchas e a corrosão.
- Experimente a proteção catódica; este método utiliza um metal de sacrifício para proteger o latão da ferrugem.
- Lavar frequentemente o latão com água e sabão neutro.
- Procure sinais precoces de corrosão para poder atuar rapidamente.
- Usar luvas para evitar que os óleos da pele provoquem corrosão.
- Conservar o latão em locais secos e com temperatura controlada.
- Evitar a exposição do latão a amoníaco, enxofre, sais e outros produtos químicos nocivos.
Tratamento da corrosão existente
- Utilizar produtos de limpeza de latão e polir com um pano macio para remover manchas e oxidação.
- Após a limpeza, adicionar revestimentos ou inibidores para evitar nova corrosão.
- Para corrosão grave, utilize sistemas de proteção catódica. Isto pode impedir os danos, especialmente em artigos de latão de grandes dimensões.
Prevenir a Dezincificação
- Escolher latão com menos de 15% de zinco.
- Lavar regularmente as linhas de água para evitar a acumulação de produtos químicos.
- Testar a qualidade da água para detetar e resolver problemas como um elevado teor de cloreto.
Conclusão
Agora já sabe que o latão não enferruja porque não tem ferro. Mas, mesmo assim, pode corroer-se em algumas condições. Coisas como a água, o sal, os produtos químicos e o stress podem afetar o desgaste dos seus artigos de latão ao longo do tempo. A boa notícia é que, com os cuidados e revestimentos corretos, é possível manter o latão com ótimo aspeto e a funcionar bem durante muito tempo. Quer seja para canalização, música ou decoração, o latão é um metal forte e útil com que pode contar.
Se alguma vez precisar de peças de latão personalizadas feitas com cuidado e precisão, DEK está aqui para ajudar. Pode contar connosco para fornecer peças duradouras e adequadas às suas necessidades.
FAQs
Com que rapidez é que o latão enferruja?
O latão não enferruja, mas pode corroer ou mudar de cor com o tempo. Se não utilizar qualquer revestimento protetor, poderá ver sinais de corrosão ou uma camada esverdeada dentro de alguns meses ou anos, dependendo do ambiente.
O brasso remove a ferrugem?
Brasso é feito para limpar e dar brilho ao latão, cobre e metais semelhantes. É bom para remover manchas e fazer com que o metal fique novamente brilhante. Mas não se destina a remover a ferrugem. Se precisar de se livrar da ferrugem, utilize um produto feito para a remoção de ferrugem.
O latão enferruja em água salgada?
O latão não enferruja porque não tem ferro. Mas se o colocarmos em água salgada, pode corroer-se com o tempo.
O latão fica verde?
Sim, o latão pode tornar-se verde com o tempo. Quando é exposto ao ar, à humidade ou a determinados químicos, pode formar uma camada verde chamada pátina. Isto acontece naturalmente e nem sempre significa que o latão está danificado.
O latão maciço enferruja?
Não, o latão maciço não enferruja porque não contém ferro. Pode ficar manchado com o tempo, mas não enferruja como o aço ou o ferro.
O latão enferruja na água?
Não, o latão não enferruja na água. O latão só pode corroer, e isso só acontece se enfrentar condições muito adversas.
Quando se trabalha com prata, é necessário compreender as suas propriedades básicas. Uma propriedade importante é a densidade da prata. Esta propriedade ajuda-o quando está a fazer peças, a verificar materiais ou a planear custos.
Neste guia, aprenderá tudo o que precisa de saber sobre a densidade da prata. Verá porque é importante, como a medir e como se compara com outros metais.
Qual é a densidade da prata?
A densidade da prata é de cerca de 10,49 gramas por centímetro cúbico. A prata é mais pesada do que muitos outros metais. Isto faz com que seja uma boa escolha quando precisa de algo forte e pesado para o seu projeto.
A prata é um dos metais mais úteis e valiosos. As pessoas adoram-na tanto pela sua beleza como pela forma como funciona bem em diferentes produtos. A sua densidade torna-a especial, pois é importante quando a prata é utilizada em moedas, jóias e muitas outras coisas.
Importância da elevada densidade da prata

A elevada densidade da prata ajuda-a a transportar muito bem a eletricidade e o calor. É por isso que é muito utilizada em componentes electrónicos e eléctricos. Porque a prata é denso, mantém-se forte sob alta pressão e não muda de forma facilmente. Isto torna-o uma boa escolha para muitos trabalhos mecânicos e industriais.
A densidade da prata também desempenha um papel importante no facto de ser tão valiosa. É uma das razões pelas quais a prata é utilizada em jóias, moedas e investimentos. A alta densidade da prata torna-a fácil de moldar e trabalhar.
Gráfico da densidade da prata
Eis a densidade da prata em diferentes unidades:
| Medição | Densidade de prata |
| Quilogramas por milímetro | 0.0105 |
| Gramas por centímetro cúbico | 10.49 |
| Toneladas por metro cúbico | 10.49 |
| Kilorams por litro | 10.49 |
| Quilogramas por metro cúbico | 10,490 |
| Onças por polegada cúbica | 6.069 |
| Onças por pé cúbico | 10,488 |
Medição da densidade da prata

Medir a densidade da prata é uma forma simples e inteligente de verificar se ela é verdadeira. Basta dividir o peso pelo volume. Por exemplo, se uma barra de prata pesar 500 gramas e ocupar 47,68 centímetros cúbicos, a densidade será de 10,49 gramas por centímetro cúbico. Isto mostra que a prata é pura.
Esta é uma boa maneira de detetar prata falsa. Metais como zinco ou estanho são mais leves e não correspondem à densidade da prata. Com as ferramentas certas ou medidas básicas, pode detetar diferenças de peso ou tamanho e evitar ser enganado.
Factores que afectam a densidade da prata

Muitos factores podem alterar a densidade da prata. Aqui estão algumas que deve saber:
Pureza da prata: A prata pura (99,9%) tem uma densidade de cerca de 10,49 g/cm³. A prata esterlina, que é prata 92,5% e misturada com metais como o cobre, é um pouco menos densa.
Temperatura: Quando a prata aquece, expande-se e torna-se menos densa. Quando arrefece, encolhe e torna-se um pouco mais densa. Estas alterações são pequenas, mas podem ser importantes em alguns trabalhos.
Composição da liga: A prata é frequentemente misturada com outros metais para a tornar mais forte. A mistura com outros metais, como o cobre ou o paládio, pode alterar ligeiramente a densidade.
Impurezas ou contaminantes: Se a prata tiver materiais indesejáveis misturados, a densidade pode aumentar ou diminuir. Depende do tipo de impurezas que estão presentes.
Porosidade: Se a prata tiver pequenos orifícios de ar no seu interior, torna-se menos densa. Isto pode acontecer com a prata em bruto ou durante o fabrico. A porosidade torna a prata menos sólida e pode afetar a sua resistência.
Aplicações práticas da densidade da prata

Como mencionado anteriormente, a densidade torna a prata valiosa e, por isso, é útil de muitas maneiras.
- O peso e a resistência da prata tornam-na perfeita para jóias detalhadas que permanecem elegantes e mantêm a sua forma.
- As moedas de prata são sólidas e pesadas, razão pela qual os coleccionadores e os investidores gostam delas.
- A densidade da prata e a sua capacidade de transportar eletricidade tornam-na essencial na eletrónica, nos painéis solares e nos dispositivos médicos.
- Funciona bem em peças pequenas, como cablagens e interruptores, onde outros metais podem não funcionar.
- A prata ajuda os painéis solares a durarem mais tempo e a terem um melhor desempenho.
- Se está a investir, a procura crescente de prata na tecnologia e na energia mostra que é um material valioso.
Prata pura vs. ligas
A prata pura é macia, pelo que não é a melhor para objectos do dia a dia. Ao adicionar outros metais, obtém-se uma prata que dura mais tempo e se mantém melhor. Aqui estão os diferentes tipos de ligas de prata:
Prata de lei

Esta é a liga de prata mais popular. É composta por 92,5% de prata e 7,5% de outros metais, geralmente cobre. A prata esterlina é forte e duradoura, pelo que é perfeita para jóias, talheres e outros artigos que queira utilizar regularmente.
Prata para moedas
A prata para moedas era comum nas moedas dos EUA. Geralmente é 90% de prata e 10% de outros metais. Embora não seja tão forte como a prata esterlina, continua a ser utilizada em artigos como jóias e peças decorativas.
Prata mexicana
Este termo refere-se a artigos de prata fabricados no México. Geralmente contém pelo menos 92,5% de prata, tal como prata esterlinae é frequentemente utilizado para jóias e artesanato de alta qualidade.
Prata Argentium

Esta liga moderna contém prata e uma pequena quantidade de germânio. Resiste melhor ao embaciamento do que a prata esterlina. É uma boa escolha para jóias que se usam frequentemente.
Comparação das densidades da prata e de outros metais
Pode usar a tabela abaixo para comparar a prata com alguns metais comuns, para que possa decidir se precisa mesmo de usar prata.
| Metal | Densidade (g/cm³) | Descrição |
| Prata | 10.49 | A prata é bastante densa, o que a torna excelente para eletrónica, jóias, moedas e muito mais. |
| Ouro | 19.32 | O ouro é quase duas vezes mais denso do que a prata, pelo que é mais pesado e mais valioso. |
| Cobre | 8.96 | O cobre é ligeiramente menos denso do que a prata, sendo utilizado para trabalhos eléctricos e ligas. |
| Alumínio | 2.7 | O alumínio é muito mais leve do que a prata, sendo ideal para projectos leves na indústria aeroespacial e automóvel. |
| Ferro | 8 | O ferro é menos denso do que a prata, mas é barato e muito utilizado na construção. |
| Titânio | 4.54 | O titânio é mais leve do que a prata mas mais forte, sendo utilizado na indústria aeroespacial e em aplicações difíceis. |
| Chumbo | 11 | O chumbo é ligeiramente mais denso do que a prata, mas a sua toxicidade limita a sua utilização. |
| Aço inoxidável | 7.75 - 8.05 | O aço inoxidável é mais leve do que a prata, mas é forte e resistente à ferrugem, sendo utilizado em edifícios e na medicina. |
| Platina | 21.45 | A platina é mais densa do que o ouro, o que a torna um dos metais preciosos mais pesados, utilizado em jóias e produtos químicos de alta qualidade. |
Conclusão
A densidade da prata é importante porque confere certas qualidades que tornam a prata útil de diferentes formas. Se estiver a fazer jóias ou a utilizar prata em indústrias, conhecer a sua densidade pode ajudá-lo a melhorar o seu trabalho.
Compreender como a prata se compara a outros metais permite-lhe satisfazer necessidades específicas de peso, resistência e funcionamento do material.
FAQs
A prata é mais densa do que o ouro?
O ouro é mais denso do que a prata. Com uma densidade de 19,32 g/cm³, é mais pesado e mais valioso. Embora a prata seja menos densa, continua a ser suficientemente forte para ser utilizada em moedas, talheres e algumas aplicações industriais.
Qual é a densidade relativa da prata em comparação com a da água?
A densidade relativa da prata é de cerca de 10,49, o que significa que é 10,49 vezes mais densa do que a água. Este facto torna a prata estável e consistente para o mesmo volume.
O que significa uma onça troy no investimento em prata?
Uma onça troy equivale a 31,1035 gramas. É a unidade padrão utilizada para as moedas e barras de prata.
O ferro é um metal forte que se utiliza em muitas coisas, como edifícios, máquinas e ferramentas. É uma boa escolha porque é resistente e fácil de moldar quando aquecido. Se quiser derreter ou unir ferro, precisa de saber o ponto de fusão do ferro. Isto ajuda-o a aquecê-lo da forma correta e a evitar erros.
Neste guia, ficará a saber porque é que o ponto de fusão é importante e como o pode utilizar quando trabalha com ferro.
Qual é o ponto de fusão do ferro?
O ferro puro derrete a cerca de 1.538°C (2.800°F). Isto é muito quente porque os átomos do ferro estão bem unidos e é necessário muito calor para quebrar essas ligações.
Mas o ponto de fusão pode mudar um pouco. Se o ferro tiver outros materiais misturados, como carbono ou outros metais, pode derreter a uma temperatura mais baixa ou mais alta. Por isso, verifique sempre o tipo de ferro que está a utilizar.
Pontos de fusão de diferentes tipos de ferro

Abaixo encontra-se uma tabela onde se pode ver a diferença entre os pontos de fusão dos diferentes tipos de ferro.
| Tipo de ferro | Ferro Ponto de fusão em °C |
| Ferro fundido | 1150 a 1200°C |
| Ferro forjado | 1482 a 1593°C |
| Ferro branco | 1130 a 1350°C |
| Ferro cinzento | 1150 a 1200°C |
| Ferro fundido dúctil | 1150 a 1200°C |
| Ferro maleável | 1170 a 1350°C |
Importância de conhecer o ponto de fusão do ferro no processamento de metais
Eis como o ponto de fusão do ferro é importante em diferentes processos metálicos:
Fundição
Quando se derrete ferro para o deitar em moldes, é necessário colocar o forno à temperatura correta. Se estiver demasiado frio, o ferro não fluirá bem. Se estiver demasiado quente, pode danificar o molde ou o metal. Conhecer o ponto de fusão ajuda-o a derreter o ferro apenas o suficiente para obter peças fundidas suaves e limpas.
Soldadura

Em soldaduraA soldadura é uma operação que consiste em unir peças de ferro utilizando calor. Se conhecer o ponto de fusão, pode escolher as ferramentas de soldadura e as definições de calor corretas. Isto ajuda-o a fazer soldaduras fortes sem danificar o metal.
Produção de ligas
Se estiver a misturar ferro com outros metais para fazer ligas como o aço, precisa de saber quando é que o ferro derrete. Isto ajuda-o a aquecê-lo corretamente e a misturar outros elementos da forma correta. Uma pequena alteração na temperatura pode afetar a mistura final.
Forjamento
Quando ferro forjadoO que se faz é aquecê-lo até ficar suficientemente macio para ser moldado. Isto acontece normalmente entre 900°C e 1.200°C. É um valor abaixo do ponto de fusão, mas ainda suficientemente quente para trabalhar o metal. Se ficar demasiado quente, o ferro pode ficar fraco ou danificado.
Tratamento térmico
No tratamento térmico, altera-se o comportamento do ferro através do seu aquecimento e arrefecimento de determinadas formas. O conhecimento do ponto de fusão indica-nos até que ponto podemos aquecer o ferro sem o derreter. Por exemplo, quando se recoze o ferro, aquece-se um pouco abaixo do ponto de fusão para o tornar mais macio e menos tenso.
Como a fusão do ferro afecta as suas propriedades

Eis o que acontece quando o ferro passa de sólido a líquido:
- O ferro passa de sólido a líquido. Esta é a mudança mais óbvia.
- O ferro aumenta de tamanho quando derrete. Isto torna-o menos denso.
- O ferro líquido não transporta o calor tão bem como o ferro sólido. Por isso, o calor espalha-se mais lentamente.
- O ferro também transporta mal a eletricidade na forma líquida. Não é tão bom como o ferro sólido para utilização eléctrica.
- O ferro fundido flui facilmente porque é menos espesso (baixa viscosidade). Isto torna-o ótimo para a fundição ou moldagem.
- A forma como o ferro fundido forma gotas e se espalha altera-se. Isto ajuda na soldadura e na fundição, onde o fluxo suave é importante.
- Quando o ferro é derretido, perde a sua força e rigidez. Mas quando arrefece e volta a ficar sólido, recupera essas propriedades.
- O ferro fundido reage mais com outros elementos. Pode oxidar ou misturar-se facilmente com outros metais, o que é útil para fazer ligas.
Ponto de ebulição do ferro vs. temperatura de fusão do ferro
O ponto de ebulição do ferro é muito superior ao seu ponto de fusão; esta é a temperatura a que o ferro líquido se transforma em gás.
Assim, quando aquecemos o ferro, este começa por derreter a 1,538°C. Se continuar a aquecê-lo para além dessa temperatura, acabará por ferver e transformar-se em gás a 2862°C. Normalmente, não é necessário atingir o ponto de ebulição no trabalho normal com metais.
Factores que afectam o ponto de fusão do ferro

Há várias coisas que podem alterar o ponto de fusão do ferro, e aqui estão algumas delas:
- Se o ferro tiver impurezas como o carbono, o seu ponto de fusão pode aumentar ou diminuir.
- Diferentes formas de ferro, como a austenite e a ferrite, têm diferentes pontos de fusão.
- Mais pressão faz o ferro fundir a uma temperatura mais elevada. Menos pressão pode fazer com que o ferro derreta a uma temperatura mais baixa.
- A adição de elementos como o níquel, o crómio ou o manganês altera o ponto de fusão do ferro
- O tamanho dos grãos de ferro pode alterar ligeiramente o seu ponto de fusão porque afecta a resistência global do material.
- A forma como se aquece o ferro, por exemplo, através do recozimento, pode alterar a sua estrutura interna, o que afecta o ponto de fusão.
Como fundir o ferro
A fusão do ferro é um processo com etapas específicas, e eis como funciona:
- Começa por obter matérias-primas como sucata ou minério de ferro.
- Certifique-se de que as matérias-primas estão limpas e isentas de quaisquer impurezas ou contaminantes.
- Escolha o forno correto para o trabalho. Pode utilizar um forno de cúpula, de jato, de arco elétrico ou de indução, dependendo das suas necessidades.
- Colocar as matérias-primas no forno. Adicionar calcário, coque ou outro agente fundente para ajudar a remover as impurezas.
- Ligue o forno e aqueça os materiais até cerca de 1.538°C, que é o ponto de fusão ideal. Certifique-se de que o calor é constante e uniforme.
- Mantenha-se atento ao processo de fusão para se certificar de que o ferro se transforma num líquido completo. Ajuste a temperatura e o fluxo conforme necessário para evitar o sobreaquecimento.
- À medida que o ferro derrete, as impurezas formam uma escória à superfície. Remova esta escória para manter o ferro fundido puro.
- Quando o ferro estiver completamente derretido, bata no forno para verter o ferro derretido em conchas ou moldes. Controlar o fluxo para evitar salpicos.
- Deixar arrefecer o ferro fundido nos moldes ou nas conchas. Se necessário, pode utilizar o arrefecimento controlado ou o recozimento para obter a forma correta.
- Uma vez arrefecido, verifique a qualidade e a consistência do ferro. Também pode mandar testá-lo para se certificar de que cumpre as normas.
Aplicações do ferro com base no ponto de fusão
Eis como as propriedades físicas do ferro são utilizadas em diferentes domínios:
Construção e infra-estruturas

O ferro é necessário para fabricar aço, que é utilizado na construção de pontes, arranha-céus e caminhos-de-ferro. O aço é forte e pode suportar cargas pesadas. Também suporta as mudanças de temperatura sem se degradar, pelo que é perfeito para estruturas de longa duração.
Maquinaria e fabrico
O ferro é também utilizado em ferramentas e peças para máquinas, uma vez que consegue suportar calor e pressão elevados sem perder a sua resistência. Isto torna-o perfeito para equipamento pesado, utensílios de cozinha e moldes utilizados no fabrico. Garante que tudo funciona bem em condições difíceis.
Indústria automóvel
Nos automóveis, o ferro contribui para a resistência ao calor. O ferro fundido é frequentemente utilizado em peças do motor porque mantém o calor e resiste ao desgaste. Isto torna-o importante para peças como blocos de motor e cambotasajudando os automóveis a funcionar sem problemas e a durar mais tempo.
Aplicações ambientais
A capacidade do ferro de resistir a altas temperaturas também o torna útil no domínio das energias renováveis. É utilizado em permutadores de calor e sistemas solares térmicos, ajudando a melhorar a eficiência energética e a contribuir para soluções energéticas sustentáveis.
Tecnologias emergentes e materiais avançados

Superligas à base de ferro são utilizados em peças como lâminas de turbinas e componentes aeroespaciais. Estes materiais podem suportar calor extremo, razão pela qual são importantes em indústrias onde a fiabilidade e o desempenho são necessários.
Comparação do ponto de fusão do ferro com outros pontos de fusão de metais
Pode comparar o ponto de fusão do ferro com o de outros metais para saber qual deles deve ser utilizado no seu projeto. Consulte a tabela abaixo.
| Metal | Ponto de fusão (°C) | Ponto de fusão (°F) |
| Alumínio | 660.3°C | 1,220.5°F |
| Cobre | 1,984°C | 3,623°F |
| Ouro | 1,064°C | 1,947°F |
| Prata | 961.8°C | 1,763°F |
| Chumbo | 327.5°C | 621.5°F |
| Níquel | 1,455°C | 2,651°F |
| Titânio | 1,668°C | 3,034°F |
| Zinco | 419.5°C | 787.1°F |
| Platina | 1,768°C | 3,214°F |
| Molibdénio | 2,623°C | 4,753°F |
| Tungsténio | 3,422°C | 6,192°F |
| Cobalto | 1,495°C | 2,723°F |
| Magnésio | 650°C | 1,202°F |
| Paládio | 1,555°C | 2,831°F |
| Ródio | 1,964°C | 3,567°F |
Conclusão
Pode ver-se que o ferro funde a uma temperatura ligeiramente superior à de muitos outros metais. É por isso que as ligas de ferro também tendem a ter pontos de fusão mais elevados.
Em DEKajudaremos a escolher a liga metálica certa para o seu projeto. Contacte-nos agora e obtenha um orçamento gratuito.
FAQs
Qual é o ponto de fusão do ferro em Fahrenheit?
O ferro funde-se a cerca de 2.800°F.
Qual é o ponto de fusão do cloreto de ferro?
Existem diferentes tipos de cloreto de ferro. O cloreto de ferro(II) (FeCl₂) funde a cerca de 605°C (1.121°F). O cloreto de ferro(III) (FeCl₃) funde a cerca de 172°F (78°C).
Qual é o ponto de fusão do ferro em Kelvin?
O ferro funde-se a cerca de 1.811 K.
Porque é que o ponto de fusão do ferro é tão elevado?
O ferro tem fortes ligações entre os seus átomos. Por esse motivo, é necessário muito calor para quebrar essas ligações e transformá-lo de sólido em líquido. É por isso que o ponto de fusão do ferro é tão elevado.
If you build or work on cars, you know how important metal parts are. Most of those parts come from flat sheets of metal that are cut, bent, and joined together.
In this guide, I’ll explain what automotive sheet metal fabrication is, how it’s done, and why it matters.
Basics of Sheet Metal Fabrication
You start by picking the right metal based on what you need, such as strength, light weight, or rust resistance.
Then, you cut, bend, and shape the metal. You can use tools like lasers or waterjets for cutting. Bending helps you form it without changing the amount of metal.
Next, you join the parts using welding, rivets, or glue, depending on how strong and neat it needs to be.
Last, you finish it with paint, powder, or planting to make it look better and last longer.
Sheet Metal Fabrication in the Automotive Industry

Cars started with wooden chassis, similar to horse-drawn carriages, but wood couldn’t bend well. The brief history of metal fabrication and its use in automobiles changed when Ford used steel for the 1908 Model T, and Dodge built the first all-steel car body in 1914. This made cars safer and stronger. By the 1970s, aluminum was used for lighter, more fuel-efficient parts.
Today, you still see fabrico de metais everywhere in automotive manufacturing. Sheet metal is used for doors, fenders, and hoods because it’s strong and safe. You also rely on metal parts for engine brackets and mounts, which must be made exactly right to keep the car working well.
Thanks to new technologies like hydroforming, car makers can now shape metal into complex designs, helping build cars that are sleek, fast, and efficient.
Types of Sheet Metals Used in Automotive Fabrication
Here are some common metals you’ll use in automotive fabrication:
Alumínio
Aluminum is lightweight and resistant to corrosion. It’s one of the most common metals for car parts because it has a high strength-to-weight ratio. This means your car parts will be lighter, which helps reduce fuel use and lowers the carbon footprint. Even with less weight, the parts will still be strong. You’ll find aluminum in parts like hoods, doors, and fenders.
Aço inoxidável

Aço inoxidável is strong, durable, and looks good. It’s often used for parts like exhaust pipes, body panels, and seat frames.
Cold Rolled Steel
Cold-rolled steel is strong and accurate in size and finish. You’ll use it for parts like door panels, frame rails, brackets, and interior components, such as seat frames and dashboard structures.
Chapa galvanizada
Galvanized steel is coated with zinc to resist corrosion. It’s perfect for car parts like body panels and chassis.
Titânio
Titanium is a strong, corrosion-resistant metal that works well for parts dealing with heavy loads or harsh conditions. It’s also heat-resistant, that is why it is ideal for parts exposed to high temperatures. However, it’s expensive, so you’ll mostly use it for high-end custom parts.
Cobre
Copper is great for electrical parts because it has excellent electrical conductivity. It’s also good for parts that need to handle heat, like radiators and heat exchangers.
Magnésio
Magnesium is a lightweight metal with a great strength-to-weight ratio, just like aluminum. It also has good thermal conductivity. You’ll use magnesium in parts like steering wheels, instrument panels, and transmission cases.
Sheet Metal Fabrication Techniques for Automotive Parts
Sheet metal fabrication includes different methods to create parts with unique shapes. Some of these methods are used during the design of car sheet metal parts.
Sheet Metal Cutting Techniques

These methods help cut sheet metal into smaller parts of various sizes:
Corte a laser
Laser cutting is often used for car parts because it’s very precise. A focused laser beam melts and vaporizes the sheet metal to create a clean cut.
When CNC technology is used, laser cutting becomes even more accurate. This makes it ideal for car parts with complex designs. It’s also compatible with many materials and is commonly used for parts like body panels and engine components.
Corte a plasma
Corte a plasma uses high-velocity ionized gas (plasma) to melt and blow away the metal, cutting the sheet. It’s great for cutting thick metal sheets, so it’s often used for making car frames.
Shearing

Shearing uses a shearer, which applies a downward force to cut the sheet metal.
Unlike laser and plasma cutting, shearing is less precise, so it’s best for car parts that don’t need tight measurements. Examples include brackets and supports.
Sheet Metal Forming Techniques
Forming techniques like bending and stamping help you shape materials into parts.
Dobragem

Bending is a common technique where a press brake machine is used to bend sheet metal into angles and curves. The machine applies force at specific points to form the desired shape. Bending is great for making auto parts like brackets, frames, and doors with complex designs.
Estampagem
Stamping or pressing shapes sheet metal by pressing it into a die. There are different types of stamping, like blanking, punching, and embossing. Stamping is best for making high-volume parts like body panels and brackets.
Sheet Metal Joining Techniques
In the automotive industry, joining techniques like welding and riveting are used to combine sheet metal parts.
Soldadura

Welding uses heat to join two or more pieces of metal. Common types of welding are spot welding, MIG weldinge Soldadura TIG. Welding is ideal for joining similar materials and creating strong, durable parts like car chassis, frames, and body panels. It’s fast and efficient.
Riveting
Riveting joins two different metals by creating holes in both pieces, inserting a rivet, and deforming the rivet to hold the parts together. This cold joining process creates a strong, permanent bond. Riveting is great for joining parts made of different materials that need strength and durability.
Applications of Sheet Metal Fabrication Parts in the Automotive Industry
Sheet metal fabrication is used in three main ways:
Car Bodies and Frames

Sheet metal fabrication is perfect for making car bodies and frames. These parts need to be strong and precise, no matter the design or material. With sheet metal techniques, you can use materials like high-strength steel and aluminum alloys to create durable, lightweight car bodies and frames.
Car Customization
You can use sheet metal fabrication to make customized parts for different cars. This helps cater to different customer preferences. Techniques like welding and riveting allow manufacturers to create custom body kits, exhaust systems, grille guards, fender flares, and even chassis.
Vintage Car Restoration
Sheet metal fabrication can also be used to restore classic cars to their original condition. It can help repair or replace damaged parts, replace discontinued parts, and create new interior components to enhance the car’s performance and look.
Benefits of Sheet Metal Fabrication for the Automotive Industry
Sheet metal fabrication offers many benefits for both manufacturers and consumers, and some of these benefits are discussed below.
Lightweight Cars for Better Fuel Efficiency

Sheet metal fabrication uses lightweight metals, which is a major benefit for the car industry. Lighter car parts mean the car needs less energy to move, which reduces fuel use and lowers the carbon footprint. Metals like aluminum and high-strength steel alloys are lightweight but strong, so car parts can be thinner and lighter without losing strength.
Durability and Longer Life of Parts
Using sheet metal fabrication makes car parts last longer and perform better. It helps cars handle rough conditions, like road debris, and improves crash safety by protecting passengers during collisions. Metals like steel and aluminum are strong, resistant to wear and tear, and can resist rust, so parts stay in good condition for a long time.
Customization and Design Flexibility
Sheet metal fabrication is great for making custom car parts. It allows car manufacturers to create complex shapes that improve aerodynamics, look better, and meet specific needs. With CAD, parts can be made with high precision and accuracy, ensuring a better fit and alignment.
Cost-Effective Production

Sheet metal fabrication is a cost-effective way to produce car parts. It allows manufacturers to make large quantities of high-quality parts at low costs. Using CAD technology improves precision and consistency, reduces human error, and cuts down on waste.
Since sheet metal is easy to get and costs less, manufacturers can lower production costs and make cars more affordable. Maintenance costs are also lower because sheet metal parts are easier to repair and replace.
Challenges and Tips When Choosing Automotive Sheet Metal Fabrication
Here are some challenges you might face with automotive sheet metal fabrication and tips to help:
Maintaining Precision
It’s important to keep parts precise. Even a small mistake can make a part defective, which can cause problems during assembly. To improve precision, follow industry standards and use CNC systems for processes like welding, laser cutting, and plasma cutting.
Ensuring Quality Materials

Using good-quality materials is crucial. Sheet metal should not have defects like cracks, holes, or bends, as these can weaken the part. To make sure you get good materials, choose a reliable supplier.
Managing Manufacturing Tolerances
Some parts need very tight measurements, which can increase production costs. To meet these standards, consider outsourcing to a trusted sheet metal fabrication service with the right equipment. This helps you avoid high upfront costs while still getting the parts you need.
High Quality Sheet Metal Fabrication with DEK
Em DEK, we use advanced technology, a wide range of high-quality materials, and fast turnaround times to provide solutions that fit the specific needs of the automotive industry. So if you need a partner for your metal fabrication, choose DEK for a smooth, top-quality experience.
For more information, to talk about your project, or to see how our sheet metal fabrication services can improve your automotive manufacturing, feel free to contact us. We look forward to working with you and helping you reach your manufacturing goals. Get a free quote today!
Conclusão
Precision, quality, and efficiency are key in the automotive industry, and sheet metal fabrication can help you achieve them. This article explains the process so you can decide if it’s the right fit for your needs.
FAQs
What is the thickness of automotive sheet metal?
Automotive sheet metal is usually between 18 and 22 gauge thick. The most common thickness is 20 gauge. A lower gauge number means the metal is thicker.
How does CAD improve automotive sheet metal fabrication?
CAD technology makes sheet metal fabrication more precise, faster, and cost-effective. It helps create accurate 3D models, reduces material waste, speeds up production, and allows quick design changes. CAD also improves team collaboration and ensures high-quality parts.
What are automotive sheet metal fabrication tools?
Automotive sheet metal fabrication tools include machines like laser cutters, CNC presses, stamping machines, shears, and welding equipment. These tools help shape, cut, and join metal to create parts for vehicles.
Is custom automotive sheet metal fabrication expensive?
Custom automotive sheet metal fabrication can be expensive because it requires specialized tools, skilled labor, and precise design work. The cost depends on factors like the complexity of the part, the materials used, and production volume.
One of the modern machining processes that gained attention over the years is helical milling. Whether you are a machinist, an engineer, or someone who is curious about the process, helical milling offers an interesting peek into modern manufacturing processes that are shaping our world today.
In this article, we will discuss interesting facts about helical milling. From the technical factors down to the best practices. We will give you a glimpse of this popular machining process.
What is Helical Milling?
Helical milling is an efficient machining process that uses a milling tool that moves in a spiral path. This movement allows the tool to cut both axially and radially. This process is used for creating high-precision holes, particularly on tough materials like titanium and steel.
This process combines accuracy and tool life because it reduces force, which minimizes tool damage.
Technical Factors of Helical Milling
Helical milling, being a modern machining process, may look simple and easy to understand, but its efficiency relies on several technical factors.
Understanding these factors will help us gauge helical milling’s performance, especially on extremely hard surfaces that will test its tools' tolerance.
Toolpath Generation
Toolpath generation is one of the most crucial technical factors of helical milling because this refers to the programming of the milling tool to operate according to a designed path into a workpiece.
CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software is used to make the toolpath. The toolpath will define the tool’s capability to cut the material in a specific direction and gauge its tool engagement.
Seleção de ferramentas

Helical milling’s optimum performance lies in the tools chosen to be used in the process. It is generally useful to consider three factors in choosing the tool: the type, diameter, and design.
Specialized cutters are chosen to match the hard workpiece and surfaces. That is why strong materials are strongly preferred to ensure strength and stress tolerance.
It is usually recommended that the tool diameter is greater than the milling diameter and the workpiece's helical radius by approximately 40-60%.
The preference in the flute design depends on some considerations. Multiple flutes if you want smoother cutting and surface finishes, and fewer flutes for deep holes to improve chip evacuation.
Chip Evacuation and Cooling
Heat control and chip removal are two important factors to ensure the smooth run of helical milling. An effective chip removal technique is needed because helical milling can produce piles of spiral chips that can clog deep holes and may cause tool damage.
Ensuring that the tool maintains a cool temperature is highly important because it reduces the stress on the tool.
Coolants and air blasts are needed to prolong tool life and ensure a smooth surface finish on every material.
Parâmetros de corte
The effective execution of helical milling also lies in the cutting parameters. These factors can significantly impact the result and the efficiency of the process.
O spindle speed, feed rate, axial depth, and helix angle must be carefully balanced to ensure efficiency and quality results.
Helical Milling Benefits
Helical milling is a modern hole-making process that delivers precision and quality results. Below is a rundown of the benefits of the highly popular machining process used by many industries today.
High-quality Holes
The gradual spiral motion of the tool used in helical milling is a huge contributing factor to the quality of the holes it produces, resulting in smooth finishes, superior quality holes, and uniform results in terms of diameters. This approach avoids common issues in the material and also the tool used for the process.
Hole Sizes Versatility
The one thing that sets helical milling apart from traditional drilling is that it has the capability to produce holes in different sizes using just one tool.
The trick is done by making adjustments to the radius of the hole and not to the tool itself. This benefit saves you more time because there is no need to change tools just to achieve a desired result.
Materials Flexibility
Helical milling’s ability to cut through even the hardest material is proof that it is an effective process that took traditional drilling to a whole new level. Helical milling works even on the most challenging materials, like hardened steel and titanium, without the risk of excessive stress on the tool.
The balanced force and heat make the process reliable for the tough materials that are commonly used in the medical and aeroespacial industries.
Lower Cutting Forces
Helical reduces the stress on the machine, the tool, and the surface itself. The gradual and evenly distributed cutting makes it an effective technique to use on hard materials and even on delicate surfaces.
Longer Tool Life

The balanced heat and forces used for this process ensure a longer life for the tool since it will not be exposed to excessive stress and overheating. The gradual approach to drilling will also not cause damage to the cutters. And the best part is that longer tool life means lower operational costs.
Helical milling is helpful and effective for industries that use hard materials like steel and titanium.
Efficiency on Chip Control
An efficient chip removal is essential in milling, not just to ensure a smooth finish but to save time on trying to unclog holes filled with chips that may even affect the final result.
Helical milling offers effective chip removal because of the tool’s spiral motion and with the use of an air blast while cutting.
Balanced Machining Temperature
Thanks to helical milling’s lower heat dispersion, incidents of overheating the tool can be avoided. Hence, the tool and the workpiece are safe from any damage.
Helical Milling Uses

Peças para automóveis
O automotive industry requires consistency. Manufacturing of automotive parts and components requires high-tolerance holes and cavities that helical milling can produce.
Helical milling’s capability to deliver consistent machining of holes and pockets using fewer tools also makes it capable of working on high-volume production.
Dispositivos médicos
With the medical industry’s need to have precise and burr-free holes for their medical devices, helical milling’s efficiency is the top-notch choice. From implants to stainless steel surgical tools, the intricate process of helical milling is helpful for their industry’s demands.
Aeroespacial
This industry’s demand for high-standard components and their use of hard steel and titanium is because to their standard of material integrity. That’s where helical milling’s expertise comes in.
Helical milling can also handle complex demands based on the critical safety standards of the industry.
Fresagem de roscas

Helical milling is being used for thread milling due to its capability to produce holes that meet their high-standard criteria for making valves and engine parts.
Plus, helical milling’s flexibility in working with challenging materials.
Mold Making
Molds have deep cavities and contours. Helical milling can keep up with the deep, intricate details of materials that are needed in this industry.
Manufacturing and Prototyping
The manufacturing industry demands flexibility and efficiency even in mass production. The ability to produce without frequent tool changes is helpful in production without sacrificing quality.
Energia
The energy industry’s demand for pipeline fittings and valves. These parts need to withstand harsh conditions and high pressure. And that’s where they can use helical milling’s advantage in terms of dealing with challenging materials.
Challenges and Considerations

Helical milling is a modern technique in machining processes, yet it is still prone to challenges based on multiple factors.
Understanding these challenges and considerations will help you think whether this process will work for your demands.
Toolpath Programming Challenges
Creating the needed spiral motion for the tool will be done with the help of software that streamlines the process. But any issues that the software encounters will deeply affect the process and the result.
It can result in poor quality products and tool damage.
The solution is to ensure that you develop perfect software that will cover the parameters.
Tool Deflection
Tool deflection is not as complicated as the programming challenges, but it sure affects the quality of the workpiece. It results in inaccurate holes and a low-quality surface finish, and even damages to the tool.
Material Limitations
Helical milling can handle complex projects and hard materials. The constant process of dealing with extra challenging materials like titanium can eventually damage the tool.
Formulating a comprehensive parameter to avoid tool damage will at least help avoid it from happening earlier than expected.
Machine Capability
The success and best results of a process highly depend on the machine’s power and capabilities. Not all machines are created equal. Some can be prone to misalignment that may eventually cause malfunction.
Choosing a machine that can work in a variety of complexities, pressures, and rigidities will assure you of its effectiveness in delivering accurate and quality results without the fear of machine breakdown.
Best Practices for Helical Milling
Helical milling would not be hailed as one of the most popular machining processes if not for its efficiency and high-quality output.
But just like any process, there are some practices to do to take advantage of its benefits.
Optimize Toolpath Parameters
Helical milling requires sets of speed feeds to maximize the tools and the process. Setting up proper parameters on the speed, feed, axial depth, and tool engagement will not only save you from machine or tool dysfunction but also the hassle of not meeting production needs.
Tools & Parts Monitoring
Just like any high-performing machine and tool, ensuring they are at their best always depends on your constant monitoring so you can provide proper cleanup and maintenance so the tools and parts are always back in shape.
Skill Development and Training
While the machines and tools can be at their best with regular checking and maintenance. The team handling the machine and tools, and program itself should be equipped with knowledge and skills in handling complex situations or even proper troubleshooting in case of challenges.
Providing your team with necessary training and development can assure you that everything is in good hands with your competent team.
Helical Milling vs Other Hole Making Methods
| Caraterística | Helical Milling | Perfuração | Aborrecido |
| Acabamento da superfície | Good to Excellent | Moderado | Bom |
| Tool Path | Spiral (helical) | Straight Plunge | Straight with side |
| Tool Wear Rate | Moderate to low
(if optimized) |
Moderado a elevado
(in tough materials) |
Baixa a moderada |
| Chip Evacuation | Manageable (requires air coolant) | Can be difficult in deep holes | Easier
(lower chip volume) |
| Material Suitability | Excellent (good for hard materials) | Varies (struggles with hard materials) | Good (especially in finishing applications) |
Conclusão
Helical milling is a modern and efficient process to create precise holes even on hard materials and challenging applications. With the help of the right parameters and tools, you will surely maximize the flexibility helical milling can offer to help you with your needs.
Here at DEK, we offer expert machining services, including advanced helical milling for high-precision parts. Contact us today to get started on your next project.
FAQs
Where is a helical milling operation commonly used?
Helical milling is generally used in industries that need precise holes, pockets, and entry points, even on hard and delicate materials. Those industries include automotive, aerospace, medical device, mold-making, and manufacturing and prototyping.
What is the purpose of helical gear cutting on milling machine?
Helical gear cutting creates gears with angled teeth, which provide smoother and quieter operation than straight-cut gears.
What is the advantage of using a helical plain milling cutter?
The advantage of a helical plain milling cutter is that it has angled teeth, which engage the material gradually. Because of that, it reduces vibrations and gives smoother cutting and a high-quality service finish compared to straight-tooth cutters.
What are the key features of a helical milling machine?
The key features of a helical milling machine are CNC control, helical toolpaths, rigid construction, and the ability to handle multi-axis movement. Spiral interpolation and high-precision cutting are usually supported by these machines.
Face milling vs end milling are two essential machining processes that serve different purposes to shape metals with precision. Understanding the differences between the two is crucial for choosing an efficient and appropriate method in manufacturing to help you achieve the desired surface finish of a project.
What is Face Milling?
Face milling is a machining process that uses a cutting tool called a face mill. This tool has cutting edges around the disk, and it cuts across the surface as the tool spins.
This process is used to create flat and smooth surfaces on a workpiece. Face milling is ideal for producing large flat areas with a smooth surface finish.
Face milling has provided ease for the automotive, aerospace, and general manufacturing industries and has proven its efficiency on every project.
Caraterísticas da fresagem de faces

Variety of Replaceable Cutting Inserts
With interchangeable cutters, face milling allows easy material removal and provides more accuracy and speed. The cutting load is distributed among a variety of inserts, which means it reduces stress on the tool, giving it a longer tool life.
Geometric Inserts
These inserts are designed to meet material and acabamento da superfície needs depending on the shape, profile, and angle.
Wider Tool Diameter
This feature makes face milling a cost-efficient and productive process because it enables wider coverage of surface areas.
Applications of Face Milling

Refining Surfaces
For aesthetic and precision purposes, industries like aerospace highly depend on face milling when finishing the surface of a workpiece. The process not only refines the surface but also provides uniform pieces for the project.
The tools’ aligned and perfectly synchronized process avoids flaws, resulting in a more efficient and smooth surface finish that meets the industry’s critical needs.
Refining Surfaces for Further Processes
Some projects don’t end with the surface finish. Some require further processing before reaching a certain product result. Face milling helps shorten the process with its speed and efficiency. Plus, it also provides an aesthetically presentable surface finish.
Machining Complex Surface Sizes
Custom machinery components may require complex sizes. With the help of several cutting inserts, face milling can cover even larger surface areas, depending on the needs of an industry. This time-saving and efficient process eases worries of uneven results, as the tool itself is designed to produce consistent and accurate finishes.
O que é a fresagem de topo?

End milling is a machining process that uses a cutting tool called an end mill. This process is used for tasks such as slotting, profiling, and contouring. It is a fundamental process in manufacturing widely used in industries such as the medical device industry and the automotive industry. These industries depend on end milling to shape and cut metals, wood, plastics, and even stone.
Features of End Milling
Versatile Cutting Capability
The versatile cutting capability of end milling is essential for cutting different shapes, contours, and slopes. Through this feature, you are able to cut slots and holes in complex angles.
Variety of Geometric Tools
The end mill tool comes in different shapes. These shapes are designed for surface sculpting or finishing of edges. The use of the right tool not only saves time and increases productivity, but it also delivers quality results.
Coolant and Chip Control
It is crucial to manage heat in end milling. The coolant cools down the tool and the workpiece, while the chip control removes the metal shavings from the surface, ensuring the process runs smoothly.
Applications of End Milling

Slotting and Pocketing
Slotting and pocketing are two important manufacturing processes that industries rely on for tools and molds, assembly parts, and mechanical designs.
3D Surface Machining
This process is used for curved surfaces that are often designated for custom shapes and designs. With the use of the ball nose end mill, the tip glides through the curve to contour the surface with precision.
Logo Cutting and Engraving
This process is useful for customization, branding, and labeling. It is also useful for identification, often used by industries like the defense and aerospace industries.
Pros and Cons: Face Milling vs End Milling
| Processo | Prós | Contras |
| Fresagem de faces | Ideal for surface preparations | Limited to flat surfaces |
| Excelente acabamento de superfície | Costly due to insert cutters | |
| Great on large surfaces | Not suitable for detailed finishes | |
| Stable tool engagement | ||
| Fresagem de topo | High precision and detailed | Tool engagement varies |
| Geometrical tool availability | Needs attention for chip removal | |
| Works on curves and 3D surfaces | Slow on bigger surfaces | |
| Flexible cutting directions |
How to Choose Between Face vs End Milling

Face milling and end milling are both essential process that serves different purposes, and choosing the right one depends on the needs of your project. Understanding the difference between the two will help you pick the right one for your needs.
Cutting Direction
Face milling cuts perpendicular to the workpiece, while end milling cuts on the sides and face.
As far as the tools are concerned, face mills and end mills both have a variety of interchangeable tools designed for complex shapes and contours. It is helpful to note that the face milling can work on larger surfaces, while end milling has a smaller diameter.
Chip Formation
For the chip formation, face milling produces shorter and broader chips coming from a wide and shallow cutting, while end milling produces longer and narrower chips that are usually from side cuts.
With the use of airblast and coolants, chip removal is generally easier with face milling, while it could be trickier with end milling because it is prone to chip buildup.
Tool Engagement
Face milling offers a more stable tool engagement due to the cutter’s position on the surface, while it is slightly unstable for end milling, depending on the support and tool speed when navigating through slopes and curves of surfaces.
Both are efficient processes. However, it is important to note that with end milling, a sturdy support needs to be provided to avoid the tool from shifting its focus on the surface.
Helix Angle
Face milling uses inset cutters with neutral or low helix angles, while end milling comes with high or variable helix angles depending on the material and the designed finish.
When choosing between face milling and end milling, it is helpful to understand that face milling offers the capability of removing large material at once, while end milling is designed to deliver a detailed finish.
Acabamento da superfície
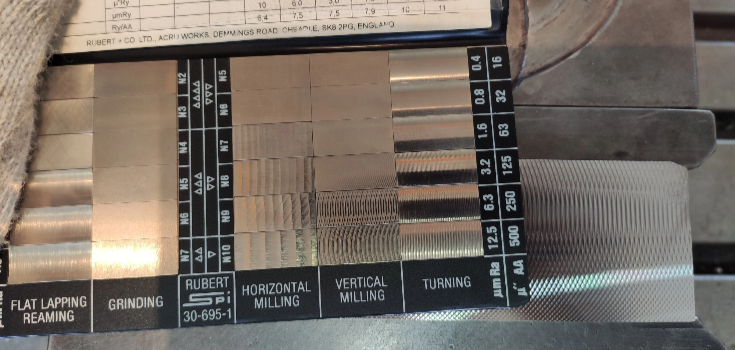
In terms of the smooth surface finish, face milling is ideal for the job, especially on larger surfaces. End milling is good for detailed surface shaping, but it may require a secondary tool for flat surface finishing.
Depending on the design of the surface, you may need to use different insert cutters and different tools for both to create your desired shapes and contours.
Quadro recapitulativo
| Caraterística | Fresagem de faces | Fresagem de topo |
| Tool Orientation | Perpendicular to the surface | Parallel to the surface |
| Cutting Surface | Mainly the outer area | End and sides |
| Aplicação | Flat surfaces | Complex shapes and slots |
| Velocidade | Elevado | Baixa |
| Precisão | Moderado | Elevado |
| Machine Type | Fresagem horizontal | Fresagem vertical |
| Material Removal Rate | Elevado | Baixa a moderada |
| Acabamento da superfície | Smooth, flat | Detailed, intricate |
Face Mill vs End Mill: Process

Face milling and end milling are two machining processes that serve different purposes and utilize different tools to shape materials.
Face milling uses the bottom cutting edges of the tool with a sweeping pattern that can cover a wider area. This process is usually used to prepare workpieces and take up parts from larger surfaces to prepare for further manufacturing processes. It increases productivity because it can cover a large surface at once.
Fresagem de topo uses the side milling process with a narrower tool. This process offers flexibility in terms of movement. It can move in different directions, which is great for contours and 3D shapes. It is good at highlighting and finishing the curves of a surface, and even engraving.
Both processes are helpful and efficient, but the choice of process to pick depends on the needs of a project or material.
When to Use Face Milling vs End Milling

Use Face Milling When:
- You need to take a workpiece from a large surface
- There is a need to take a huge block to prepare it for other processes.
- You want high material removal and a smooth finish
- The part you need to cut is not complicated and has no odd shapes or slopes.
Use End Milling When:
- The material requires holes, slots, and pockets
- The part needs detailed finishes like contours and 3D shapes
- You need a flexible tool that offers a variety of cutting directions.
- When you need to engrave on metals and other surfaces.
How Face Milling and End Milling Work Together
Face milling and end milling are two different processes that serve different purposes in machining, but both can also be used together to come up with a perfect finish to a material.
Face milling can take on the initial process of creating a flat workpiece, as it only prepares a material for further enhancements and finishes. When the material is ready, end milling can take charge of the intricate details needed, such as pockets, slots, contours, and 3D shapes. The end mill handles the final form of the material.
Conclusão
Face milling and end milling both play crucial roles in machining processes. Face milling is ideal for surface preparations, while end milling highlights the details, shapes, and features of a material. Choosing the right process depends on the design, needs, and manufacturing goals.
Here at DEK, we offer competitive milling services using both processes to help you produce high-standard and quality parts. Contact us today for a quote and let us discuss your projects with our machining experts.
