- Startseite
- Ressourcen
- What is Brittleness: A Complete Guide
What is Brittleness: Ein vollständiger Leitfaden
Brittleness is an essential material property that changes design, manufacturing, and product strength. When a material is weak, it breaks quickly without noticeable deformation. This causes understanding and awareness, which is important for safe and effective engineering.
In this blog, you will learn about what brittleness is, how it looks in different sciences, the causes, types, formulas, and examples. At the end, you will understand why brittleness is crucial and how to use brittle materials in practical applications.
What is Brittleness?
Brittleness is the feature of a material that makes it fracture or break when stress is applied, with little or no plastic deformation. A brittle material cannot absorb considerable energy before failure. Instead of stretching or bending, it instantly breaks.
What is Brittleness in Materials Science?

In materials science, brittleness is the property of a material to fracture upon application of stress, rather than deform plastically. Brittle materials show fewer slip systems even at the atomic scale. Thus, these materials have atomic structures that do not allow easy movement, leading to crack formation.
What is Brittleness in Chemistry?
Brittleness is associated with atomic bonding and microstructure in chemistry. If strong ionic or covalent bonds bind the atoms of a material in the absence of sufficient slip systems, the material does not deform under stress.
For example, take glass and ceramics, for instance. Their rigid atomic structure makes them brittle, while metals with comparatively flexible atomic bonds are usually ductile.
Types of Brittleness
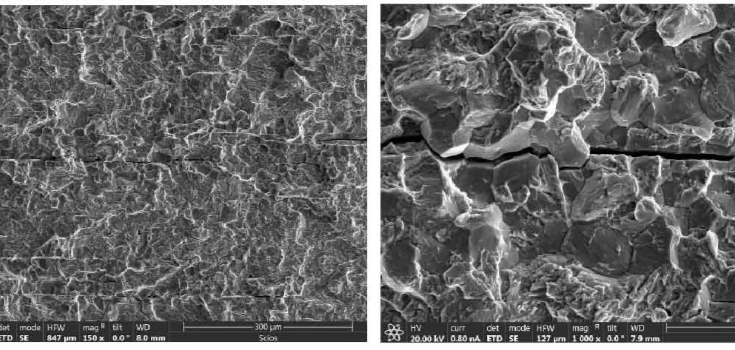
Transgranular
Transgranular brittleness occurs when cracks directly spread through the grains of a material. The cracks travel along planes of weakness in the crystal structure. Crack growth is much quicker in materials that have large grains because fewer boundaries block the distribution.
Intergranular
The intergranular brittleness path occurs along the grain boundaries. Weakening of those boundaries may result from hydrogen embrittlement, corrosion, or impurities. Cracks migrating between the grains make the material sensitive to sudden failure.
Formula for Brittleness
There is no direct formula for brittleness. Instead, brittleness is determined using ductility measurements. Ductility can be calculated as:
- Percentage Elongation = (Final Length – Original Length) ÷ Original Length × 100
- Percentage Reduction in Area = (Original Area – Final Area) ÷ Original Area × 100
The lower the ductility, the higher the brittleness.
Example of Brittleness

One of the most common examples is glass. When a glass bottle drops, it breaks suddenly into parts without any bending. Cast iron suddenly fractures under impact. Ductile metals like aluminum bend and then break. All these are signs of how brittle materials fail without any timely sheds.
When Does Brittleness of Material Occur?
Brittleness occurs in two main ways:
- Those kinds of materials that are by nature brittle, for instance, ceramics and glass.
- Ductile materials are made to become brittle through external effects like cold temperatures, impurities, or chemicals.
For example, steel at very low temperatures becomes nonductile. It fractures in a brittle way.
Causes of Brittleness
| Cause | Explanation |
| Atomare Struktur | Materials like glass possess a limited or disordered atomic plane. They cannot relieve stress, resulting in immediate cracks. |
| Strong Ionic or Covalent Bonds | In ceramics, the rigid bonding that exists does not allow the atomic movement. So the material cannot be deformed before breaking. |
| Limited Slip Systems | Fewer slip systems in materials with HCP. Elements such as graphite or magnesium contribute to a reduction of ductility and hence increase brittleness. |
| Impurities or Defects | Small flaws, voids, or inclusions within the material act as stress concentrators, triggering cracks. |
| Low Plasticity in Alloys | Alloys, like cast iron, break instantly because their structures do not provide easy paths for plastic deformation. |
Different Brittle Materials
Glas

Glas is the most common brittle material. In general, because of its amorphous atomic structure, it does not have any ordered planes for stress relief. Under stress, the weak points concentrate it.
This concentration of crack formation then leads to the sudden dispersal of crack propagation throughout the material. That is why it is noted that when most glass objects are dropped, such as bottles or windows, they break into sharp fragments without warning.
Keramik
Keramik like porcelain, brick, or pottery are strong yet brittle. They contain very strong ionic and covalent bonds that prevent atoms from sliding past one another. While they confer great resistance to heat and durability, the rigidity of ceramics limits plastic deformation.
Graphit
Graphite, a crystalline form of carbon, also shows breakability. It has a hexagonal close-packed (HCP) crystal shape with only three slip systems, which causes atomic movement to be limited.
Atoms are strongly bonded, but weak interlayer bonds make the structure prone to splitting. This combination tells you why graphite can break or collapse under stress. It is commonly used in pencils, electrodes, and lubricants.
Alloys With Low Plasticity
Some alloys, like cast iron and titanium alloys, are brittle due to their crystal structures and poor ductility. Alloys having the HCP structure, such as Magnesium and titanium, are being made more brittle as they contain fewer slip systems.
On the other hand, alloys with FCC structures, such as copper, exhibit large ductility. Cast iron is one common example where brittleness, in spite of strength and wear resistance, causes sudden fracture at elevated loads.
How Do Brittle Materials Behave Under Tensile Loading?
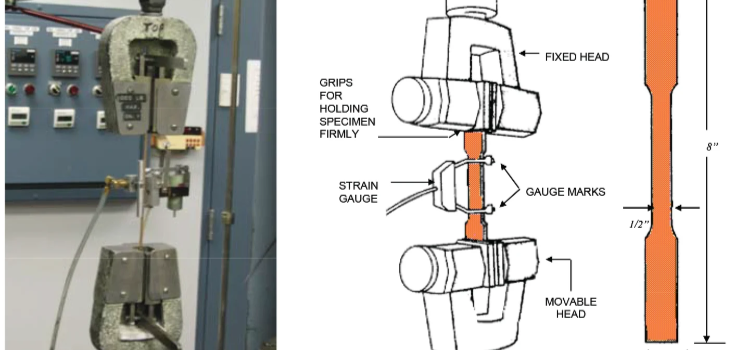
Brittle materials break under tensile stress without any stretching. They have low exhaustion capacity and high solidity. Formation of cracks and further propagation of these cracks takes place across or laterally along their particles, which will lead to failure of the material. A situation that occurs without any warning.
How Do Brittle Materials Behave Under Compression Loading?
Brittle materials move toward failure either by crumbling or by splitting across the weak planes when loaded in compression. Instead of bending, they break very suddenly. Hence, concrete under compression will crumble along its internal microcracks.
Importance of Identifying Brittleness
Identifying brittleness is important in engineering design. Brittle materials may provide high abilities but fail without warning. Understanding the materials’ brittleness authorizes you to select safer, ductile replacements or adjust operating conditions.
For example, in mechanical engineering, avoiding brittle failure is crucial in load-bearing parts.
Schlussfolgerung
Brittleness is a key property that affects how materials respond under stress. By understanding examples such as glass, ceramics, graphite, and alloys, you can make informed material choices in engineering and design.
At DEK, we specialize in helping you evaluate material properties, including brittleness. Our team provides precise manufacturing solutions, testing, and analysis to ensure your projects achieve both safety and durability. Kontakt today to optimize your designs with reliable material expertise.
FAQs
How is brittleness determined?
Brittleness is the property determined through tensile tests, where ductility is also measured. Less stretching and decreased area indicate high brittleness.
What is the opposite of brittleness?
Ductility is just the opposite of brittleness. Ductile materials can deform plastically before spontaneously breaking.
Is brittleness a physical property?
Yes, brittleness is a physical property of a material, which determines the characteristics of a material in terms of how it breaks under stress.
What is the difference between “fragile” and “brittle?”
Fragile means easily breakable. However, brittle specifically says hard, rigid, and fractures with little or no plastic deformation.
