- Startseite
- Ressourcen
- Kühlkörpertypen: Welche wählen Sie?
Heat Sink Types: Which One to Choose?
When your electronics get hot, you need something to cool them down. That’s where heat sinks help. But not all heat sinks are the same.
There are many heat sink types, and each one works best in different situations. In this post, you’ll learn about the most common types so you can choose the right one for your project.
What is a Heat Sink?
A heat sink helps keep your device cool. It takes heat from hot parts like the CPU and spreads it out. It is usually made of metal like aluminum or copper.
The heat moves from the part to the heat sink by touching it, which is called conduction. Then the heat goes into the air through a process called convection. Sometimes a fan helps move the air faster; this is called forced convection. If there is no fan, the air moves on its own, which is natural convection.
Heat sinks have fins to increase surface area so more heat can move into the air. This keeps your device from overheating.
How Does a Heat Sink Work?
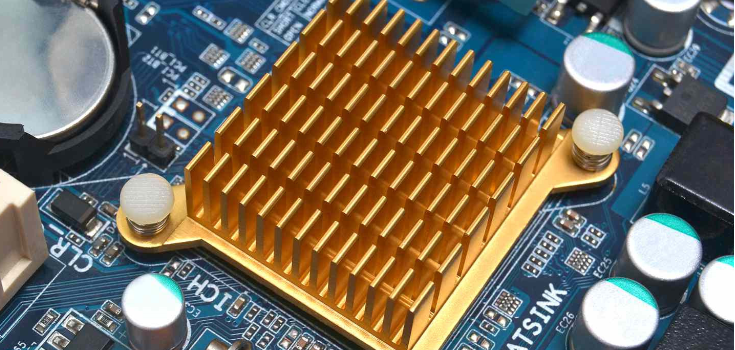
When your electronic parts work, they get hot because electricity flows through them. You need to get rid of this heat so the parts don’t get too hot and break. A heat sink helps by taking in the heat and spreading it over a bigger area, so the heat can go into the air better.
You attach the heat sink to the hot part using a special material like thermal paste or a pad. This material helps move the heat from the part to the heat sink.
After the heat moves into the heat sink, it cools down by moving into the air around it. The bigger the heat sink’s surface, the better it cools.
Good cooling is very important for your electronics, and heat sinks are a key part of that.
Airflow-Based Heat Sink Classification
The two main categories of heat sinks are the following:
Passive Heat Sink

A passive heat sink does not use a fan or any other forced airflow. It is more reliable because it has no moving parts. For example, sometimes the heat sink is part of the device’s case. The heat moves from the parts that get hot to the walls of the case. These walls usually have fins that touch the outside air to help cool down.
Active Heat Sink
An active heat sink has a powered device, like a fan or blower, near the heat sink surface. It can also use pumped liquid to carry heat away. Because it forces air or liquid over the fins, it cools better. This means the heat sink can be smaller and lighter.
Manufacturing-Based Heat Sink Classification
Let’s look at 6 common types of heat sinks based on manufacturing process:
Extruded Heat Sinks
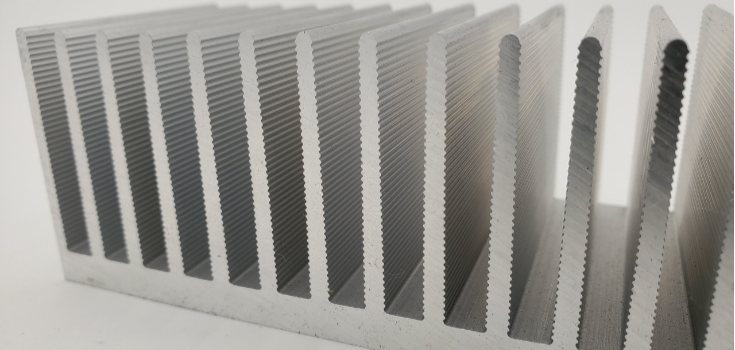
Most heat sinks are made by pushing aluminum through a shaped hole. This method works for many uses. You get low cost and can easily make them fit your needs. Their performance can be low or high, but you can only make them as wide as the machine allows.
Bonded Heat Sinks
You usually use these when you need big heat sinks. You can mix different metals for the base and fins, like Aluminium and copper. This helps the heat sink work better without making it too heavy. They work okay to well but cost a lot.
Skived Heat Sinks
These heat sinks are made from one solid piece of copper. You can design them in many shapes, and they have lots of thin fins. This gives you more surface to cool things down. They work pretty well but are heavy and must be placed carefully.
Stamped Heat Sinks
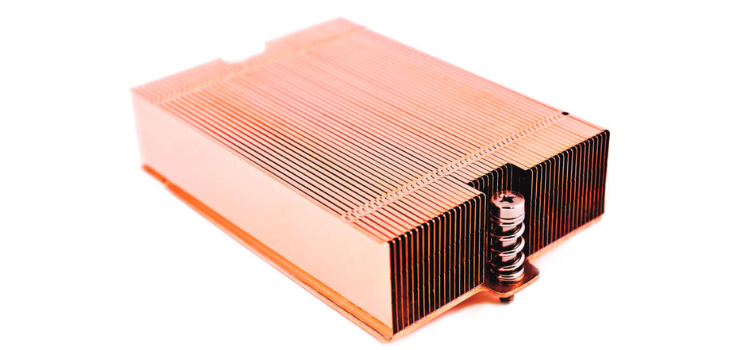
Here, metal fins are pressed out and then attached to the base. You use these for devices that don’t need much cooling. They cost very little because they are easy to make, but they don’t cool very well.
Forged Heat Sinks
These are made by pressing aluminum or copper hard into shape. You can make many things this way, and it doesn’t cost much. They work okay, but don’t allow for many design options.
CNC Machined Heat Sinks
You can make very detailed and complex shapes with this method. They cool very well, but it costs a lot, and it takes time, so it’s not good for making many pieces quickly.
Water-Cooled Heat Sink Classification
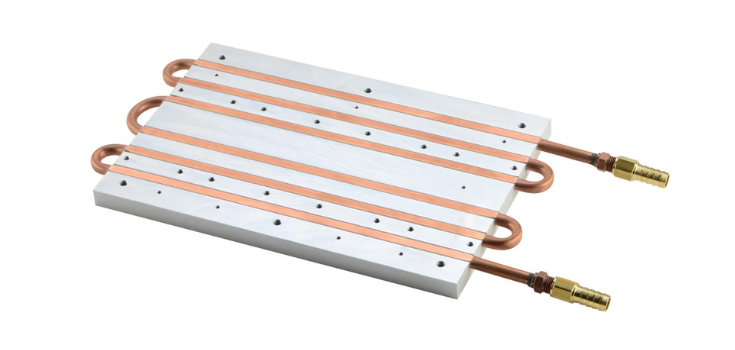
This classification might sound confusing, but it just means three types: solid metal heat sinks, heat sinks with two-phase devices, and heat sinks that use pumped liquid.
Solid Metal Heat Sinks
These heat sinks have a solid base that takes in heat and metal fins that send the heat out to the air around them. The base and fins can be made from different metals, like copper or aluminum, especially for electronics. These are usually the cheapest heat sinks you can get.
Pumped Liquid Heat Sink
These heat sinks use a pump to move liquid away from the hot part. The liquid goes to a cold plate that touches the heat source, then flows back to the fins to cool down. This way cools very well, but is the least reliable for electronics.
Two-Phase Heat Sink

Two-phase heat sinks use devices like vapor chambers and heat pipes to help move heat better. These devices carry heat very well, so your heat sink works better overall. Heat pipes move heat from the hot part to fins far away.
Vapor chambers spread heat across the base to cool fins nearby. These heat sinks are almost as reliable as solid metal ones but cost a little more.
Heat Sink Materials
As mentioned earlier, heat sinks are usually made of aluminum and copper. Here are more details:
Aluminum Heat Sink
Aluminum is light, easy to make, and doesn’t cost much. That’s why it’s a great choice for most heat sinks. The common types are called alloys 6061 and 6063, but purer types like 1050 and 1100 move heat a little better. Aluminum moves heat about half as well as copper. This means heat can’t travel as far from the hot part through the heat sink base.
Copper Heat Sink
Copper moves heat much better, about twice as well as aluminum. You use copper when you need better cooling. A common type of copper used is called CDA110.
But copper is heavier, like about three times heavier, and costs twice as much as aluminum. It also works a bit slower than aluminum. Some heat sinks mix the two metals: copper for the base and aluminum for the fins.
What Can Heat Sinks Be Used for?
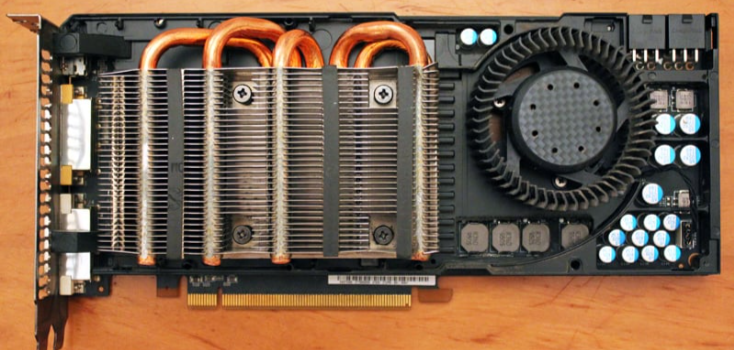
Heat sinks are important to keep your PC parts, like CPUs and GPUs, cool. But you can also use heat sinks for many other things, like:
- Motherboards
- Solid-state drives and relays
- Power transistors
- Gedruckte Leiterplatten (PCBs)
- Inside or outside laptops
- Amplifiers
How to Choose the Right Heat Sink

When you want to select the best types of heat sink for a computer, you need to think about your setup and how much cooling you need. The first step is to understand some basics about your device.
Here’s what you should think about when choosing CPU heat sink types or other heat sinks:
- How much power does your part use? This is called TDP or thermal design power. It tells you the maximum heat your CPU or GPU can make in watts. This helps you know how hot it can get when working hard.
- How cool is your CPU, or do other parts need to be to work their best?
- How much space do you have to put the heat sink? Heat sinks come in many sizes, from small to large.
- Which heat sink design or shape will cool your computer best?
- Whether you need an active heat sink (with fans or moving parts) or a passive one (no moving parts).
- How much money do you want to spend on your heat sink?
Schlussfolgerung
Choosing the right heat sink depends on what you need for your device. Think about how much heat you need to remove, the space you have, and your budget.
If you need help choosing or designing the right heat sink, contact DEK today. We offer custom heat sink solutions made just for your needs.
